
에 의해 TCMVET | 2024년 12월 13일 | 개 암 및 종양
Nose cancer in dogs, also known as nasal cancer, is a relatively rare but aggressive condition that affects the nasal cavity or sinuses. While it accounts for less than 1% of all canine cancers, its severity lies in its invasive nature and the difficulty of early detection. This article delves into the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and supportive care for dogs battling nose cancer.
What Is Nose Cancer in Dogs?
Canine nose cancer primarily involves tumors that develop within the nasal passages or sinuses. The most common type is 선암, but other forms like squamous cell carcinoma, fibrosarcoma, or osteosarcoma can also occur. This condition typically affects older dogs, with larger breeds appearing to be at a slightly higher risk.
징후 및 증상
Early signs of nasal cancer can be subtle and are often mistaken for respiratory infections or allergies. As the disease progresses, the symptoms become more pronounced. Look out for the following:
- Persistent Nasal Discharge
Unilateral discharge (affecting one nostril) that is bloody or mucoid in nature is a hallmark symptom.
- Frequent Sneezing
Chronic sneezing that doesn’t improve with treatment could indicate nasal irritation from a tumor.
- 얼굴 붓기
Swelling around the nose, eyes, or forehead may occur as the tumor invades surrounding structures.
- Breathing Difficulty
Snoring or noisy breathing might indicate a blockage in the nasal passages.
- Nose Bleeds (Epistaxis)
Intermittent or continuous bleeding from the nose is often reported.
- 신경학적 증상
If the tumor extends into the brain, symptoms like seizures, disorientation, or behavioral changes may appear.
- Loss of Appetite and Weight Loss
As with many cancers, systemic effects can lead to reduced food intake and weight loss.
진단
Diagnosing nose cancer involves a thorough evaluation, including:
- 신체 검사: A vet may check for asymmetry in the face or abnormal sounds during breathing.
- Rhinoscopy: A small camera inserted into the nasal passages helps visualize the tumor.
- 이미징: X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs provide detailed views of the tumor and its spread.
- 생검: Tissue samples confirm the type and severity of the cancer.
치료 옵션
Treatment depends on the tumor’s size, type, and stage, as well as the overall health of your dog. Options include:
- 방사선 치료
Radiation is the most effective treatment for nasal cancer, aiming to shrink the tumor and alleviate symptoms. While it may not cure the cancer, it can significantly improve quality of life.
- 수술
Surgical removal of the tumor is challenging due to the complex anatomy of the nasal area but may be attempted in specific cases.
- 화학 요법
Chemotherapy is less commonly used but might be recommended for certain tumor types or as an adjunct to other treatments.
- 완화 치료
When curative treatment isn’t an option, palliative care focuses on relieving pain and discomfort through medications, including anti-inflammatories, pain relievers, and nasal decongestants.
Natural Therapies for Supportive Care
Incorporating holistic approaches alongside conventional treatments can enhance your dog’s comfort:
- 허브 보충제
같은 허브 심황 (curcumin) and 복사 뼈 are believed to have anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties.
- 식단 조정
A high-quality, low-carbohydrate diet supports overall health and reduces inflammation.
- CBD 오일
Cannabidiol may help manage pain and reduce anxiety in dogs with advanced cancer.
예후와 삶의 질
The prognosis for canine nose cancer depends on factors like tumor type and stage at diagnosis. With radiation therapy, many dogs experience symptom relief and extended survival times, often ranging from 8 to 18 months. Without treatment, the disease progresses quickly, often within weeks to a few months.
개를 지원하는 방법
- 증상 모니터링: Keep track of changes in breathing, eating, or energy levels.
- Frequent Vet Visits: Regular check-ups ensure your dog’s condition is monitored closely.
- Provide Comfort: Soft bedding, a quiet environment, and easy access to food and water make a big difference.
마지막 생각들
Canine nose cancer is a daunting diagnosis, but with timely intervention and a comprehensive care plan, you can give your dog the best possible quality of life. Always consult with your veterinarian to explore treatment options tailored to your dog’s specific needs.

에 의해 TCMVET | 2024년 12월 13일 | 개 암 및 종양
Kidney cancer in dogs, while rare, is a serious condition that can significantly impact your furry friend’s quality of life. Recognizing the signs early can make a big difference in treatment outcomes. In this article, we’ll explore the telltale signs of kidney cancer, discuss why it often goes unnoticed, and provide insights into supportive care options.
What Is Kidney Cancer in Dogs?
Kidney cancer refers to abnormal cell growth in one or both kidneys. In dogs, renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of kidney cancer, primarily affecting older dogs. While its exact cause remains unclear, genetic predisposition and exposure to toxins may play a role.
The Subtle Signs: Why Kidney Cancer Often Hides in Plain Sight
Kidney cancer symptoms can be easily mistaken for less severe issues like urinary tract infections or general aging. This overlap in signs often delays diagnosis. Here’s what to look out for:
- Frequent Urination or Difficulty Urinating
An increase in urination frequency or visible discomfort while urinating may indicate kidney stress or obstruction caused by a tumor.
- Blood in the Urine (Hematuria)
Bright red or dark brown urine is a key warning sign that something might be wrong with your dog’s kidneys.
- 식욕 상실
A sudden lack of interest in food, combined with weight loss, may signal systemic issues related to kidney function.
- 혼수
If your dog seems unusually tired or unwilling to engage in daily activities, this could point to the underlying fatigue caused by kidney dysfunction.
- Abdominal Swelling
Swelling in the abdomen could result from a large kidney tumor pressing against other organs.
- Vomiting and Nausea
As kidney cancer progresses, toxins build up in the blood, leading to gastrointestinal distress.
How Kidney Cancer Differs from Other Conditions
Many of the above symptoms mimic those of kidney disease, bladder infections, or even diabetes. However, in kidney cancer, these signs are more persistent and worsen over time without treatment.
The Role of Diagnostics
Detecting kidney cancer requires a combination of tests:
- Ultrasounds and X-rays provide imaging of potential tumors.
- Blood Tests reveal abnormal kidney function or anemia.
- Urinalysis can identify microscopic blood or cancer cells.
Veterinarians may also recommend a biopsy to confirm the type and severity of the cancer.
Natural Therapies for Supportive Care
While surgical removal of the affected kidney is often the primary treatment, holistic approaches can complement traditional methods to improve your dog’s quality of life.
- 허브 요법
Herbs like Chuanxiong (Szechuan Lovage) may help enhance circulation and reduce inflammation around the kidneys.
- 식단 조정
A low-phosphorus, high-quality protein diet supports kidney function and reduces the workload on the remaining kidney.
- CBD 오일
Cannabidiol may help manage pain and reduce stress in dogs undergoing treatment.
Prevention Tips: Can You Reduce the Risk?
While it’s impossible to completely prevent kidney cancer, there are steps you can take to promote overall kidney health:
- Provide fresh, filtered water.
- Avoid exposure to known carcinogens like pesticides.
- Schedule regular veterinary check-ups, especially for senior dogs.
수의사 진료 시기
If you notice any of the symptoms above, consult your veterinarian immediately. Early intervention can lead to better outcomes, whether through surgery, chemotherapy, or palliative care.
마지막 생각들
Kidney cancer in dogs is a challenging diagnosis, but being proactive about your dog’s health can make a world of difference. By recognizing subtle changes and seeking timely medical advice, you can ensure your beloved pet receives the care and comfort they deserve.

에 의해 TCMVET | 2024년 12월 12일 | 개 암 및 종양
Anal cancer in dogs, while relatively uncommon, is a serious condition that requires prompt attention. The most frequently diagnosed type is anal sac adenocarcinoma, a malignant tumor that arises from the anal glands. This type of cancer is known for its aggressive nature and potential to spread to other parts of the body. In this article, we explore the symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and outlook for dogs affected by anal cancer.
What Is Anal Cancer in Dogs?
Anal cancer refers to the development of malignant tumors in or near the anal glands. These glands, located on either side of the anus, play a role in secreting fluids used for marking territory. When cancer develops in these glands, it often grows rapidly and can metastasize to nearby lymph nodes, lungs, or other organs.
Symptoms of Anal Cancer in Dogs
The symptoms of anal cancer in dogs can vary depending on the size and location of the tumor and whether it has spread. Common signs include:
- Lumps or Swelling: A noticeable mass or swelling near the anus.
- 배변 곤란: Straining, pain, or changes in stool shape due to the tumor obstructing the rectum.
- 출혈: Blood around the anus or in the stool.
- Scooting or Licking: Dogs may scoot on the ground or excessively lick the area due to discomfort.
- Hypercalcemia Symptoms: Increased thirst, frequent urination, lethargy, or weakness caused by elevated calcium levels in the blood.
- Weight Loss and Loss of Appetite: Advanced cases may lead to systemic symptoms like weight loss and a reduced appetite.
How Is Anal Cancer Diagnosed?
To diagnose anal cancer, veterinarians use a combination of:
- 신체 검사: Checking for lumps, swelling, or discomfort in the anal area.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration or Biopsy: Sampling the tumor tissue to confirm malignancy.
- 혈액 검사: Identifying hypercalcemia or other abnormalities.
- 이미징: X-rays, ultrasound, or CT scans to determine the extent of the cancer and check for metastasis.
Treatment Options for Anal Cancer in Dogs
The treatment approach depends on the stage and spread of the cancer. Common options include:
- 수술: The primary treatment for localized anal cancer is surgical removal of the tumor and potentially affected lymph nodes.
- 방사선 치료: Often used in combination with surgery to target residual cancer cells.
- 화학 요법: Recommended for cases where the cancer has metastasized or as an adjunct to other treatments.
- 완화 치료: For advanced cases, pain management, dietary adjustments, and supportive care can improve quality of life.
Prognosis for Dogs with Anal Cancer
The outlook for dogs with anal cancer depends on several factors, including the size of the tumor, whether it has spread, and the treatment provided. Early detection and aggressive treatment improve survival rates, with many dogs experiencing extended periods of good quality of life post-treatment. However, advanced cases with metastasis have a less favorable prognosis.
Caring for a Dog with Anal Cancer
As a pet owner, providing a supportive and comfortable environment for your dog is essential. Follow these tips:
- 정기 수의사 방문: Schedule frequent check-ups to monitor your dog’s condition.
- Nutrition: Offer a balanced diet tailored to your dog’s needs during treatment.
- 통증 관리: Work with your vet to ensure your dog is comfortable.
- 정서적 지원: Provide love and reassurance to help your dog cope with the stress of treatment.
결론
While anal cancer in dogs is aggressive, early detection and a comprehensive treatment plan can make a significant difference in outcomes. Stay vigilant for symptoms and seek veterinary care promptly if you notice any unusual signs. With the right support and care, your dog can maintain a good quality of life, even during challenging times.
에 의해 TCMVET | 2024년 12월 12일 | 개 암 및 종양
Kidney cancer in dogs is relatively rare but can significantly impact a dog’s health when it occurs. The symptoms often appear gradually, making early detection challenging. Awareness of the potential signs can help pet owners seek timely veterinary care.
Common Symptoms of Kidney Cancer in Dogs
- Increased Thirst and Urination (Polydipsia and Polyuria):
- Excessive drinking and urination may indicate impaired kidney function due to the tumor.
- Loss of Appetite:
- Dogs with kidney cancer often experience a decrease in appetite, leading to weight loss.
- Weight Loss:
- Even with normal food intake, weight loss can occur as the body expends energy fighting the disease.
- Vomiting and Nausea:
- Kidney dysfunction caused by cancer can lead to toxins building up in the blood, causing gastrointestinal issues.
- Abdominal Pain or Swelling:
- Tumors may cause visible swelling or discomfort when the abdomen is touched.
- Blood in Urine (Hematuria):
- Urine may appear pink or red due to bleeding from the tumor.
- Lethargy:
- Dogs with kidney cancer may exhibit reduced energy levels and reluctance to engage in normal activities.
- Difficulty Breathing:
- In advanced cases, tumors may press against surrounding organs, causing respiratory issues.
- 창백한 잇몸:
- Anemia, often associated with kidney cancer, can cause gums to appear pale.
- Bad Breath (Uremic Breath):
- A buildup of toxins in the blood due to reduced kidney function can result in an ammonia-like odor.
수의사 진료 시기
If your dog exhibits any combination of these symptoms, it’s essential to seek veterinary attention promptly. While these signs are not exclusive to kidney cancer, they often indicate a serious underlying health issue that requires diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis of Kidney Cancer in Dogs
A veterinarian will typically use the following methods to confirm kidney cancer:
- 신체 검사: To detect swelling or discomfort.
- 소변검사: To check for blood or abnormal substances in the urine.
- 혈액 검사: To evaluate kidney function and detect any abnormalities.
- 이미징: Ultrasound, X-rays, or CT scans can identify tumors and their extent.
- 생검: A sample of the tumor may be taken to confirm its nature.
치료 및 예후
Treatment options depend on the tumor type and stage but may include:
- 수술: Removal of the affected kidney (nephrectomy) if the cancer is localized.
- 화학 요법: For certain types of cancer, chemotherapy may slow progression.
- 지원 관리: Pain management, hydration, and nutritional support to maintain quality of life.
Early detection improves treatment outcomes, so regular veterinary check-ups are vital, especially for senior dogs.
By recognizing these symptoms and acting quickly, you can provide your dog with the best chance of receiving effective care and maintaining a good quality of life.
에 의해 TCMVET | 2024년 12월 11일 | 개 암 및 종양
플라스틱은 식품 용기부터 가정용품, 심지어 털복숭이 친구를 위해 디자인된 제품에 이르기까지 우리 일상 생활의 모든 곳에 있습니다. 하지만 이 겉보기에 무해한 소재가 우리 개들의 건강에 위협이 될 수 있을까요? 새로운 연구에 따르면 특정 유형의 플라스틱에 장기간 노출되면 개에게 암 위험이 증가할 수 있다고 합니다. 과학을 살펴보고 애완동물 주인이 애완동물을 보호하기 위해 할 수 있는 일을 알아보겠습니다.
플라스틱의 숨겨진 위험
많은 유형의 플라스틱에는 비스페놀 A(BPA), 프탈레이트, 폴리염화비닐(PVC)과 같은 유해한 화학 물질이 포함되어 있습니다. 이러한 화학 물질은 종종 플라스틱을 내구성, 유연성 또는 투명하게 만드는 데 사용됩니다. 그러나 플라스틱이 가열되거나 긁히거나 분해될 때 특히 음식, 물 또는 환경으로 스며들 수 있습니다.
동물의 경우, 이러한 화학 물질은 내분비 교란 물질로 작용하여 호르몬 기능을 방해할 수 있습니다. 장기간 노출되면 세포 변화, 산화 스트레스, 심지어 종양 형성으로 이어져 암 발병 가능성이 높아질 수 있습니다. 매일 씹고, 핥고, 다양한 물질과 가까이 접촉하는 습관이 있는 개의 경우 위험이 더 커집니다.
개를 위한 플라스틱 노출의 일상적 출처
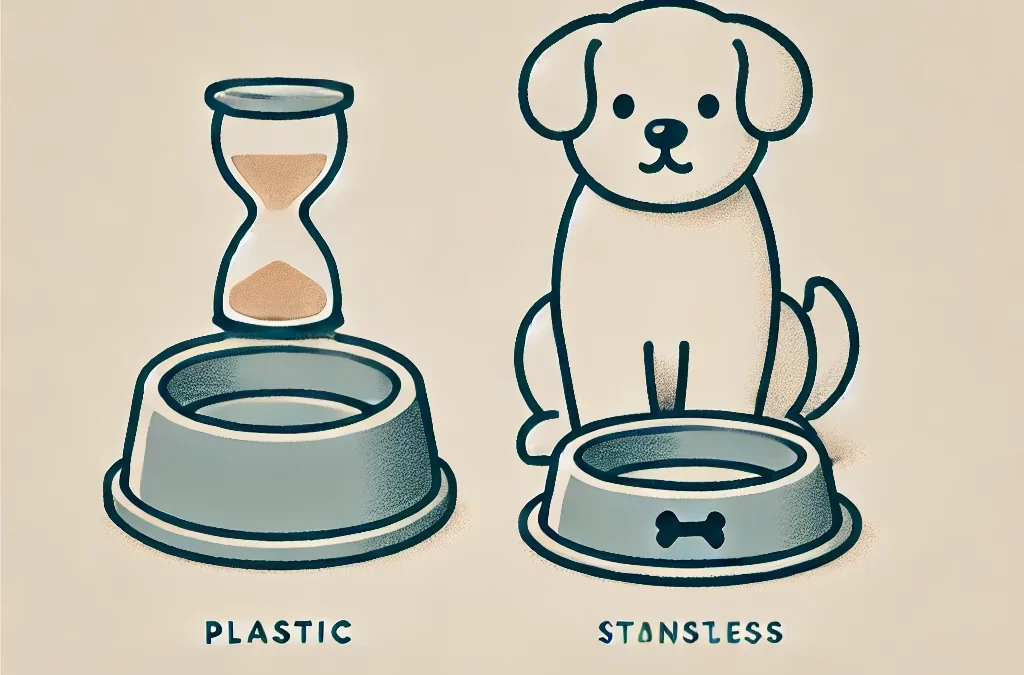
- 음식과 물 그릇: 많은 개 주인들이 자신도 모르게 플라스틱 그릇을 사용하는데, 그릇에서 특히 긁히거나 햇빛에 노출되면 유해 물질이 방출될 수 있습니다.
- 씹는 장난감: 품질이 낮은 플라스틱 장난감에는 규제되지 않은 물질이 포함되어 있는 경우가 많으며, 이러한 물질은 삼키거나 많이 씹을 경우 위험할 수 있습니다.
- 포장: 반려견 간식, 사료 및 기타 제품은 종종 플라스틱 포장재에 보관되는데, 이로 인해 화학 물질이 음식으로 스며들어 들어갈 수 있습니다.
- 가정용품: 개는 집 주변에 있는 용기부터 가구까지 플라스틱 물체와 자주 접촉하게 됩니다.
플라스틱과 관련된 암 위험
플라스틱 노출과 개 암 사이의 직접적인 연관성은 아직 연구 중이지만, 인간과 동물 연구의 증거는 우려스러운 관계를 나타냅니다. 개에서 유방 종양, 고환암, 림프종과 같은 암은 플라스틱에서 발견되는 것을 포함한 환경 독소의 영향을 받을 수 있습니다. 작은 품종이나 기존 건강 문제가 있는 개는 특히 취약할 수 있습니다.
플라스틱 노출을 줄이기 위한 단계
애완동물 주인은 개가 유해한 플라스틱에 노출되는 것을 최소화하기 위해 사전 조치를 취할 수 있습니다.
- Safer Bowls로 전환: 플라스틱 그릇 대신 음식과 물을 담을 수 있는 스테인리스 스틸, 세라믹, 유리 그릇을 사용하세요.
- 고품질 장난감을 선택하세요: 독성이 없고 BPA가 없는 장난감이나 고무와 같은 천연 소재로 만든 장난감을 선택하세요.
- 보관 재고: 개 사료와 간식은 원래 플라스틱 포장재에 담아두지 말고, 유리나 스테인리스 스틸로 만든 기밀 용기에 보관하세요.
- 집을 검사하세요: 개가 씹거나 삼킬 수 있는 저품질 플라스틱 품목에 대한 접근을 제한하세요.
- 플라스틱 가열을 피하세요: 플라스틱 용기에 담긴 음식이나 간식을 전자레인지에 넣지 마세요. 열로 인해 화학 물질이 침출될 가능성이 높아집니다.
보다 안전한 표준을 옹호하다
개인적인 선택을 넘어, 애완동물 주인은 애완동물 제품 산업에서 더 나은 안전 기준을 옹호할 수 있습니다. 무독성 소재와 지속 가능한 관행을 우선시하는 브랜드를 지원하는 것은 강력한 메시지를 전달합니다. 또한, 제품 리콜이나 새로운 연구에 대한 정보를 얻는 것은 숨겨진 위험으로부터 개를 보호하는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다.
더 큰 그림
플라스틱은 현대 생활의 유비쿼터스한 부분이지만, 잠재적인 건강 영향은 무시할 수 없습니다. 우리 개들에게 해로운 플라스틱에 대한 노출을 줄이는 것은 장기적 건강과 웰빙을 지원하는 간단하면서도 효과적인 방법입니다. 의식적인 선택을 하고 인식을 확산함으로써 우리는 반려동물이 더 행복하고 건강한 삶을 살 수 있도록 할 수 있습니다.

에 의해 TCMVET | 2024년 12월 11일 | 개 암 및 종양
개에 관해서는 크기가 중요합니다. 하지만 우리가 일반적으로 생각하는 방식만은 아닙니다. 큰 개는 힘 때문에 존경받고 작은 개는 매력 때문에 존경받지만, 최근 연구에서는 개의 크기와 암 발병 위험 사이에 놀라운 연관성이 있다는 사실을 발견했습니다. 이 흥미로운 연관성을 파헤쳐보고 반려동물 주인에게 어떤 의미가 있는지 살펴보겠습니다.
크기와 암 위험의 과학
연구에 따르면 그레이트 데인, 베르네스 마운틴 도그, 로트바일러와 같은 대형견은 소형견에 비해 특정 암에 걸릴 가능성이 더 높습니다. 하지만 왜 그럴까요? 그 답은 생물학에 있습니다. 대형견은 더 빨리 자라고 몸에 세포가 더 많습니다. 이렇게 세포 활동이 증가하면 돌연변이가 발생할 가능성이 높아지고, 이는 암으로 이어질 수 있습니다.
반면, 치와와와 다크스훈트와 같은 소형견은 암 위험이 낮은 경향이 있지만 완전히 면역이 있는 것은 아닙니다. 비만세포종과 같은 특정 암은 여전히 소형견에게 영향을 미칠 수 있으며, 이는 종종 크기보다는 유전적 소인 때문입니다.
빠른 성장: 양날의 검
대형견은 강아지 시절에 급격한 성장 폭발을 겪으며, 몸에 엄청난 부담을 줍니다. 이 빠른 성장은 세포 분열의 안정성을 떨어뜨릴 수 있으며, 이는 시간이 지남에 따라 비정상적인 세포 행동의 위험을 증가시킵니다. 또한 대형견의 대사 요구는 노화를 가속화하여 나이가 들면서 암을 포함한 질병에 더 취약해질 수 있습니다.
장수와 암 위험
작은 개는 종종 큰 품종보다 훨씬 오래 산다. 이 장수 덕분에 작은 개는 연령 관련 질환을 앓을 시간이 더 많지만, 성장과 세포 교체가 더 느리기 때문에 큰 품종에서 흔히 볼 수 있는 조기 발병 암으로부터 보호받을 수도 있다. 반면, 큰 개의 수명이 짧은 것은 종종 어린 나이에 공격적인 암이 더 많이 발생하는 것과 상관관계가 있다.
애완동물 주인이 할 수 있는 일
반려동물 주인은 개의 크기에 관계없이 암 위험을 최소화하기 위한 사전 조치를 취할 수 있습니다. 정기적인 수의과 검진, 균형 잡힌 식단, 적절한 운동 루틴이 필수적입니다. 대형견의 경우 비만이 암 위험을 더욱 악화시킬 수 있으므로 건강한 체중을 유지하는 데 특별한 주의를 기울여야 합니다. 소형견은 크기와 관련된 암에 덜 취약하지만 유전적 위험을 조기에 식별하기 위한 유전자 검사의 이점이 있습니다.
"크기가 중요하다"의 재정의
크기와 암 위험 사이의 연관성은 우리가 개 관리에 대한 접근 방식을 재고하도록 도전합니다. 우리는 개의 크기를 바꿀 수 없지만, 그것이 건강에 어떤 영향을 미치는지 이해하면 정보에 입각한 결정을 내리는 데 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 품종 선택에서 관리 일상 맞춤화에 이르기까지, 이러한 지식은 애완동물 주인이 털복숭이 친구에게 길고 건강한 삶을 살 수 있는 최상의 기회를 제공할 수 있도록 합니다.
결국, 크든 작든 모든 개는 사랑과 관심, 그리고 적극적인 건강 관리를 받을 자격이 있습니다. 정보를 얻음으로써 우리 모두는 암 위험을 줄이고 우리의 반려견이 잘 지내도록 하는 데 역할을 할 수 있습니다.







