
par TCMVET | 13 décembre 2024 | Cancer et tumeurs du chien
Le cancer du nez chez le chien, également appelé cancer nasal, est une maladie relativement rare mais agressive qui affecte la cavité nasale ou les sinus. Bien qu'il représente moins de 1% de tous les cancers canins, sa gravité réside dans sa nature invasive et la difficulté de détection précoce. Cet article se penche sur les symptômes, le diagnostic, les options de traitement et les soins de soutien pour les chiens qui luttent contre le cancer du nez.
Qu’est-ce que le cancer du nez chez le chien ?
Le cancer du nez chez le chien concerne principalement les tumeurs qui se développent dans les voies nasales ou les sinus. Le type le plus courant est adénocarcinome, mais d'autres formes comme le carcinome épidermoïde, le fibrosarcome ou l'ostéosarcome peuvent également survenir. Cette affection touche généralement les chiens plus âgés, les races de grande taille semblant présenter un risque légèrement plus élevé.
Signes et symptômes
Les premiers signes du cancer du nez peuvent être subtils et sont souvent confondus avec des infections respiratoires ou des allergies. À mesure que la maladie progresse, les symptômes deviennent plus prononcés. Soyez attentif aux signes suivants :
- Écoulement nasal persistant
Un écoulement unilatéral (affectant une narine) de nature sanglante ou mucoïde est un symptôme caractéristique.
- Éternuements fréquents
Des éternuements chroniques qui ne s’améliorent pas avec le traitement pourraient indiquer une irritation nasale due à une tumeur.
- Gonflement du visage
Un gonflement autour du nez, des yeux ou du front peut survenir lorsque la tumeur envahit les structures environnantes.
- Difficulté respiratoire
Un ronflement ou une respiration bruyante peuvent indiquer un blocage des voies nasales.
- Saignements de nez (épistaxis)
Des saignements de nez intermittents ou continus sont souvent signalés.
- Symptômes neurologiques
Si la tumeur s’étend au cerveau, des symptômes tels que des convulsions, une désorientation ou des changements de comportement peuvent apparaître.
- Perte d'appétit et perte de poids
Comme pour de nombreux cancers, les effets systémiques peuvent entraîner une réduction de l’apport alimentaire et une perte de poids.
Diagnostic
Le diagnostic du cancer du nez nécessite une évaluation approfondie, comprenant :
- Examen physique:Un vétérinaire peut vérifier une asymétrie du visage ou des sons anormaux lors de la respiration.
- Rhinoscopie:Une petite caméra insérée dans les voies nasales permet de visualiser la tumeur.
- Imagerie:Les radiographies, les tomodensitométries ou les IRM fournissent des vues détaillées de la tumeur et de sa propagation.
- Biopsie:Les échantillons de tissus confirment le type et la gravité du cancer.
Options de traitement
Le traitement dépend de la taille, du type et du stade de la tumeur, ainsi que de l'état de santé général de votre chien. Les options incluent :
- Radiothérapie
La radiothérapie est le traitement le plus efficace contre le cancer du nez. Elle vise à réduire la tumeur et à atténuer les symptômes. Même si elle ne guérit pas le cancer, elle peut améliorer considérablement la qualité de vie.
- Chirurgie
L’ablation chirurgicale de la tumeur est difficile en raison de l’anatomie complexe de la région nasale, mais peut être tentée dans des cas spécifiques.
- Chimiothérapie
La chimiothérapie est moins couramment utilisée mais peut être recommandée pour certains types de tumeurs ou en complément d’autres traitements.
- Soins palliatifs
Lorsque le traitement curatif n’est pas une option, les soins palliatifs se concentrent sur le soulagement de la douleur et de l’inconfort au moyen de médicaments, notamment des anti-inflammatoires, des analgésiques et des décongestionnants nasaux.
Thérapies naturelles pour les soins de soutien
L'intégration d'approches holistiques aux traitements conventionnels peut améliorer le confort de votre chien :
- Suppléments à base de plantes
Des herbes comme curcuma (curcumine) et astragale On pense qu’ils ont des propriétés anti-inflammatoires et stimulantes pour le système immunitaire.
- Adaptations diététiques
Une alimentation de haute qualité et faible en glucides favorise la santé générale et réduit l’inflammation.
- Huile de CBD
Le cannabidiol peut aider à gérer la douleur et à réduire l’anxiété chez les chiens atteints d’un cancer avancé.
Pronostic et qualité de vie
Le pronostic du cancer du nez chez le chien dépend de facteurs tels que le type de tumeur et le stade au moment du diagnostic. Grâce à la radiothérapie, de nombreux chiens ressentent un soulagement des symptômes et une survie prolongée, allant souvent de 8 à 18 mois. Sans traitement, la maladie progresse rapidement, souvent en quelques semaines ou quelques mois.
Comment soutenir votre chien
- Surveiller les symptômes:Suivez les changements dans la respiration, l’alimentation ou les niveaux d’énergie.
- Visites fréquentes chez le vétérinaire:Des contrôles réguliers permettent de surveiller de près l'état de santé de votre chien.
- Offrir du réconfort:Une litière moelleuse, un environnement calme et un accès facile à la nourriture et à l’eau font une grande différence.
Dernières pensées
Le cancer du nez chez le chien est un diagnostic difficile à poser, mais avec une intervention rapide et un plan de soins complet, vous pouvez offrir à votre chien la meilleure qualité de vie possible. Consultez toujours votre vétérinaire pour explorer les options de traitement adaptées aux besoins spécifiques de votre chien.

par TCMVET | 13 décembre 2024 | Cancer et tumeurs du chien
Le cancer du rein chez le chien, bien que rare, est une maladie grave qui peut avoir un impact significatif sur la qualité de vie de votre ami à quatre pattes. Reconnaître les signes tôt peut faire une grande différence dans les résultats du traitement. Dans cet article, nous explorerons les signes révélateurs du cancer du rein, expliquerons pourquoi il passe souvent inaperçu et donnerons un aperçu des options de soins de soutien.
Qu'est-ce que le cancer du rein chez le chien ?
Le cancer du rein désigne une croissance cellulaire anormale dans un ou les deux reins. Chez le chien, le carcinome à cellules rénales est le type de cancer du rein le plus courant, touchant principalement les chiens âgés. Bien que sa cause exacte reste inconnue, une prédisposition génétique et une exposition à des toxines peuvent jouer un rôle.
Les signes subtils : pourquoi le cancer du rein se cache souvent à la vue de tous
Les symptômes du cancer du rein peuvent facilement être confondus avec des problèmes moins graves comme des infections urinaires ou le vieillissement général. Ce chevauchement des signes retarde souvent le diagnostic. Voici ce à quoi il faut faire attention :
- Miction fréquente ou difficulté à uriner
Une augmentation de la fréquence des mictions ou une gêne visible lors de la miction peuvent indiquer un stress rénal ou une obstruction causée par une tumeur.
- Sang dans les urines (hématurie)
Une urine rouge vif ou brun foncé est un signe d’alerte clé indiquant qu’il pourrait y avoir un problème avec les reins de votre chien.
- Perte d'appétit
Un manque soudain d’intérêt pour la nourriture, associé à une perte de poids, peut signaler des problèmes systémiques liés à la fonction rénale.
- Léthargie
Si votre chien semble inhabituellement fatigué ou peu disposé à participer à ses activités quotidiennes, cela pourrait indiquer une fatigue sous-jacente causée par un dysfonctionnement rénal.
- Abdominal Swelling
Un gonflement de l’abdomen peut résulter d’une grosse tumeur rénale qui exerce une pression sur d’autres organes.
- Vomissements et nausées
À mesure que le cancer du rein progresse, les toxines s’accumulent dans le sang, entraînant des troubles gastro-intestinaux.
En quoi le cancer du rein diffère-t-il des autres maladies ?
Bon nombre des symptômes ci-dessus ressemblent à ceux d’une maladie rénale, d’une infection de la vessie ou même du diabète. Cependant, dans le cas du cancer du rein, ces signes sont plus persistants et s’aggravent avec le temps sans traitement.
Le rôle du diagnostic
La détection du cancer du rein nécessite une combinaison de tests :
- Les échographies et les rayons X permettent d’obtenir des images des tumeurs potentielles.
- Les analyses de sang révèlent une fonction rénale anormale ou une anémie.
- L’analyse d’urine peut identifier du sang microscopique ou des cellules cancéreuses.
Les vétérinaires peuvent également recommander une biopsie pour confirmer le type et la gravité du cancer.
Thérapies naturelles pour les soins de soutien
Bien que l’ablation chirurgicale du rein affecté soit souvent le traitement principal, des approches holistiques peuvent compléter les méthodes traditionnelles pour améliorer la qualité de vie de votre chien.
- Remèdes à base de plantes
Des herbes comme le Chuanxiong (livèche du Sichuan) peuvent aider à améliorer la circulation et à réduire l’inflammation autour des reins.
- Adaptations diététiques
Un régime pauvre en phosphore et riche en protéines de haute qualité soutient la fonction rénale et réduit la charge de travail du rein restant.
- Huile de CBD
Le cannabidiol peut aider à gérer la douleur et à réduire le stress chez les chiens soumis à un traitement.
Conseils de prévention : pouvez-vous réduire le risque ?
Bien qu’il soit impossible de prévenir complètement le cancer du rein, vous pouvez prendre certaines mesures pour favoriser la santé globale des reins :
- Fournir de l’eau fraîche et filtrée.
- Évitez l’exposition à des substances cancérigènes connues comme les pesticides.
- Prévoyez des contrôles vétérinaires réguliers, en particulier pour les chiens âgés.
Quand consulter un vétérinaire
Si vous remarquez l'un des symptômes ci-dessus, consultez immédiatement votre vétérinaire. Une intervention précoce peut conduire à de meilleurs résultats, que ce soit par chirurgie, chimiothérapie ou soins palliatifs.
Dernières pensées
Le cancer du rein chez le chien est un diagnostic difficile, mais être proactif concernant la santé de votre chien peut faire toute la différence. En reconnaissant les changements subtils et en demandant rapidement des conseils médicaux, vous pouvez vous assurer que votre animal bien-aimé reçoit les soins et le confort qu'il mérite.

par TCMVET | 12 décembre 2024 | Cancer et tumeurs du chien
Le cancer anal chez le chien, bien que relativement rare, est une maladie grave qui nécessite une attention immédiate. Le type le plus fréquemment diagnostiqué est adénocarcinome du sac anal, une tumeur maligne qui provient des glandes anales. Ce type de cancer est connu pour sa nature agressive et son potentiel de propagation à d'autres parties du corps. Dans cet article, nous explorons les symptômes, le diagnostic, les options de traitement et les perspectives pour les chiens touchés par le cancer anal.
Qu’est-ce que le cancer anal chez le chien ?
Le cancer anal désigne le développement de tumeurs malignes dans ou à proximité des glandes anales. Ces glandes, situées de chaque côté de l'anus, jouent un rôle dans la sécrétion de fluides utilisés pour marquer le territoire. Lorsque le cancer se développe dans ces glandes, il se développe souvent rapidement et peut métastaser dans les ganglions lymphatiques, les poumons ou d'autres organes voisins.
Symptômes du cancer anal chez le chien
Les symptômes du cancer anal chez le chien peuvent varier en fonction de la taille et de l'emplacement de la tumeur et de sa propagation. Les signes courants comprennent :
- Bosses ou gonflements : Une masse ou un gonflement visible près de l’anus.
- Difficulté à déféquer : Effort, douleur ou changement de forme des selles dus à la tumeur qui obstrue le rectum.
- Saignement: Du sang autour de l’anus ou dans les selles.
- Scooting ou léchage : Les chiens peuvent se déplacer sur le sol ou lécher excessivement la zone en raison de l'inconfort.
- Symptômes de l'hypercalcémie : Augmentation de la soif, miction fréquente, léthargie ou faiblesse causée par des niveaux élevés de calcium dans le sang.
- Perte de poids et perte d'appétit : Les cas avancés peuvent entraîner des symptômes systémiques tels qu’une perte de poids et une diminution de l’appétit.
Comment diagnostique-t-on le cancer de l’anus ?
Pour diagnostiquer le cancer anal, les vétérinaires utilisent une combinaison de :
- Examen physique : Vérification de la présence de grumeaux, de gonflements ou d’inconfort dans la région anale.
- Aspiration à l'aiguille fine ou biopsie : Échantillonnage du tissu tumoral pour confirmer la malignité.
- Des analyses de sang: Identifier l’hypercalcémie ou d’autres anomalies.
- Imagerie : Radiographies, échographies ou tomodensitométries pour déterminer l’étendue du cancer et vérifier la présence de métastases.
Options de traitement pour le cancer anal chez le chien
L'approche thérapeutique dépend du stade et de la propagation du cancer. Les options courantes comprennent :
- Chirurgie : Le traitement principal du cancer anal localisé est l’ablation chirurgicale de la tumeur et des ganglions lymphatiques potentiellement affectés.
- Radiothérapie : Souvent utilisé en combinaison avec la chirurgie pour cibler les cellules cancéreuses résiduelles.
- Chimiothérapie : Recommandé dans les cas où le cancer a métastasé ou en complément d’autres traitements.
- Soins palliatifs : Dans les cas avancés, la gestion de la douleur, les ajustements alimentaires et les soins de soutien peuvent améliorer la qualité de vie.
Pronostic pour les chiens atteints d'un cancer anal
Les perspectives pour les chiens atteints d'un cancer anal dépendent de plusieurs facteurs, notamment de la taille de la tumeur, de sa propagation et du traitement administré. Une détection précoce et un traitement agressif améliorent les taux de survie, de nombreux chiens bénéficiant de périodes prolongées de bonne qualité de vie après le traitement. Cependant, les cas avancés avec métastases ont un pronostic moins favorable.
Prendre soin d’un chien atteint d’un cancer anal
En tant que propriétaire d'un animal de compagnie, il est essentiel de fournir un environnement favorable et confortable à votre chien. Suivez ces conseils :
- Visites vétérinaires régulières : Planifiez des contrôles fréquents pour surveiller l’état de votre chien.
- Nutrition: Offrez une alimentation équilibrée et adaptée aux besoins de votre chien pendant le traitement.
- Prise en charge de la douleur : Travaillez avec votre vétérinaire pour vous assurer que votre chien est à l’aise.
- Soutien affectif: Offrez de l’amour et du réconfort à votre chien pour l’aider à faire face au stress du traitement.
Conclusion
Bien que le cancer anal chez le chien soit agressif, une détection précoce et un plan de traitement complet peuvent faire une différence significative dans les résultats. Restez attentif aux symptômes et consultez rapidement un vétérinaire si vous remarquez des signes inhabituels. Avec le soutien et les soins appropriés, votre chien peut maintenir une bonne qualité de vie, même dans les moments difficiles.
par TCMVET | 12 décembre 2024 | Cancer et tumeurs du chien
Le cancer du rein chez le chien est relativement rare, mais il peut avoir des conséquences importantes sur la santé de l'animal lorsqu'il survient. Les symptômes apparaissent souvent progressivement, ce qui rend la détection précoce difficile. La connaissance des signes potentiels peut aider les propriétaires d'animaux à rechercher des soins vétérinaires en temps opportun.
Symptômes courants du cancer du rein chez le chien
- Augmentation de la soif et de la miction (polydipsie et polyurie) :
- Une consommation excessive d’alcool et une miction excessive peuvent indiquer une altération de la fonction rénale due à la tumeur.
- Loss of Appetite:
- Les chiens atteints d’un cancer du rein connaissent souvent une diminution de l’appétit, entraînant une perte de poids.
- Weight Loss:
- Même avec une alimentation normale, une perte de poids peut survenir car le corps dépense de l’énergie pour combattre la maladie.
- Vomissements et nausées :
- Le dysfonctionnement rénal causé par le cancer peut entraîner une accumulation de toxines dans le sang, provoquant des problèmes gastro-intestinaux.
- Douleur ou gonflement abdominal :
- Les tumeurs peuvent provoquer un gonflement visible ou une gêne lorsque l’abdomen est touché.
- Sang dans les urines (hématurie) :
- L’urine peut paraître rose ou rouge en raison du saignement de la tumeur.
- Lethargy:
- Les chiens atteints d’un cancer du rein peuvent présenter des niveaux d’énergie réduits et une réticence à s’engager dans des activités normales.
- Difficulty Breathing:
- Dans les cas avancés, les tumeurs peuvent exercer une pression sur les organes environnants, provoquant des problèmes respiratoires.
- Gencives pâles :
- L’anémie, souvent associée au cancer du rein, peut provoquer une pâleur des gencives.
- Mauvaise haleine (haleine urémique) :
- Une accumulation de toxines dans le sang due à une fonction rénale réduite peut entraîner une odeur semblable à celle de l’ammoniac.
Quand consulter un vétérinaire
Si votre chien présente une combinaison de ces symptômes, il est essentiel de consulter rapidement un vétérinaire. Bien que ces signes ne soient pas exclusifs au cancer du rein, ils indiquent souvent un problème de santé sous-jacent grave qui nécessite un diagnostic et un traitement.
Diagnostic du cancer du rein chez le chien
Un vétérinaire utilisera généralement les méthodes suivantes pour confirmer le cancer du rein :
- Examen physique : Pour détecter un gonflement ou un inconfort.
- Analyse d'urine : Pour vérifier la présence de sang ou de substances anormales dans l’urine.
- Des analyses de sang: Pour évaluer la fonction rénale et détecter d’éventuelles anomalies.
- Imagerie : L’échographie, les rayons X ou la tomodensitométrie peuvent identifier les tumeurs et leur étendue.
- Biopsie: Un échantillon de la tumeur peut être prélevé pour confirmer sa nature.
Traitement et pronostic
Les options de traitement dépendent du type et du stade de la tumeur, mais peuvent inclure :
- Chirurgie : Ablation du rein affecté (néphrectomie) si le cancer est localisé.
- Chimiothérapie : Pour certains types de cancer, la chimiothérapie peut ralentir la progression.
- Soins de soutien : Gestion de la douleur, hydratation et soutien nutritionnel pour maintenir la qualité de vie.
La détection précoce améliore les résultats du traitement. Des contrôles vétérinaires réguliers sont donc essentiels, en particulier pour les chiens âgés.
En reconnaissant ces symptômes et en agissant rapidement, vous pouvez offrir à votre chien les meilleures chances de recevoir des soins efficaces et de maintenir une bonne qualité de vie.
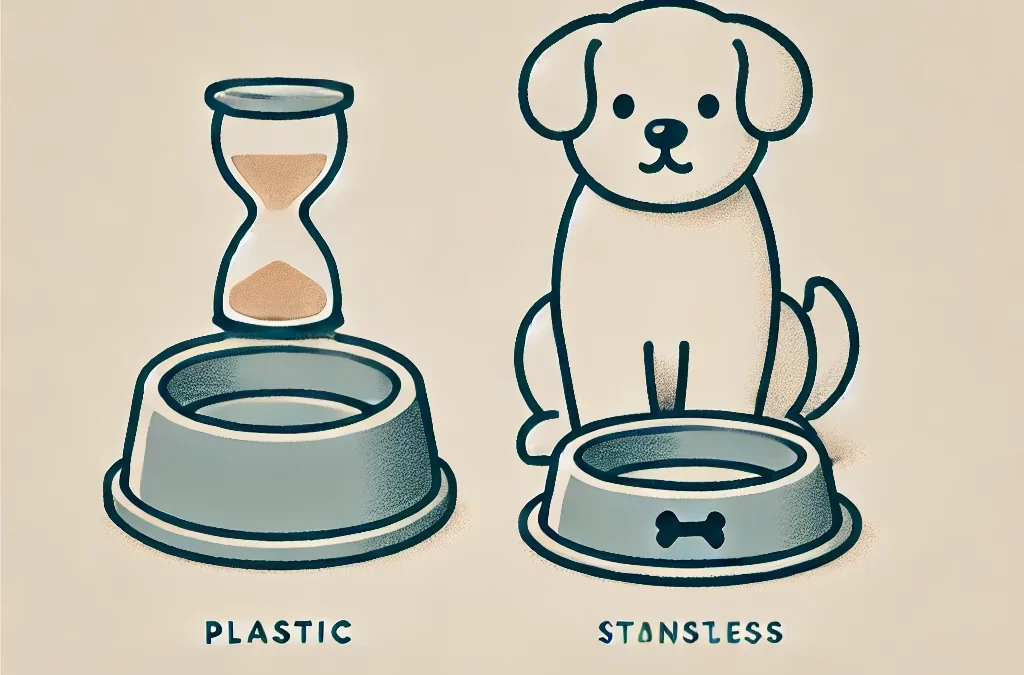
par TCMVET | 11 décembre 2024 | Cancer et tumeurs du chien
Le plastique est omniprésent dans notre vie quotidienne, des contenants alimentaires aux articles ménagers, et même dans les produits conçus pour nos amis à quatre pattes. Mais ce matériau apparemment inoffensif pourrait-il constituer une menace pour la santé de nos chiens ? De nouvelles études suggèrent qu'une exposition prolongée à certains types de plastique pourrait augmenter le risque de cancer chez les chiens. Examinons les résultats scientifiques et les mesures que les propriétaires d'animaux peuvent prendre pour protéger leurs animaux.
Les dangers cachés du plastique
De nombreux types de plastiques contiennent des produits chimiques nocifs tels que le bisphénol A (BPA), les phtalates et le chlorure de polyvinyle (PVC). Ces produits chimiques sont souvent utilisés pour rendre le plastique durable, flexible ou transparent. Cependant, ils peuvent s'infiltrer dans les aliments, l'eau ou même l'environnement, en particulier lorsque les plastiques sont chauffés, rayés ou dégradés.
Chez les animaux, ces produits chimiques peuvent agir comme des perturbateurs endocriniens, interférant avec la fonction hormonale. Une exposition prolongée peut entraîner des changements cellulaires, un stress oxydatif et même la formation de tumeurs, augmentant ainsi le risque de cancer. Pour les chiens, dont les habitudes quotidiennes incluent souvent le fait de mâcher, de lécher et d'être en contact étroit avec divers matériaux, les risques sont aggravés.
Sources quotidiennes d'exposition au plastique pour les chiens
- Bols pour la nourriture et l'eau:De nombreux propriétaires de chiens utilisent sans le savoir des bols en plastique, qui peuvent libérer des substances nocives, surtout s'ils sont rayés ou exposés au soleil.
- Jouets à mâcher:Les jouets en plastique de mauvaise qualité contiennent souvent des matériaux non réglementés qui peuvent présenter un risque s’ils sont ingérés ou mâchés de manière excessive.
- Conditionnement:Les friandises, croquettes et autres produits pour chiens sont souvent stockés dans des emballages en plastique, ce qui peut laisser pénétrer des produits chimiques dans les aliments.
- Articles ménagers:Les chiens entrent fréquemment en contact avec des objets en plastique dans la maison, des contenants aux meubles.
Risques de cancer liés au plastique
Bien que les liens directs entre l’exposition au plastique et le cancer chez les chiens soient encore à l’étude, des preuves issues de recherches sur les humains et les animaux indiquent une relation inquiétante. Chez les chiens, les cancers tels que les tumeurs mammaires, le cancer des testicules et le lymphome peuvent être influencés par des toxines environnementales, notamment celles présentes dans le plastique. Les races de petite taille ou les chiens souffrant de problèmes de santé préexistants peuvent être particulièrement vulnérables.
Mesures pour réduire l’exposition au plastique
Les propriétaires d’animaux de compagnie peuvent prendre des mesures proactives pour minimiser l’exposition de leur chien aux plastiques nocifs :
- Passez à des bols plus sûrs:Utilisez des bols en acier inoxydable, en céramique ou en verre pour la nourriture et l’eau plutôt que des bols en plastique.
- Choisissez des jouets de haute qualité:Optez pour des jouets non toxiques, sans BPA ou fabriqués à partir de matériaux naturels comme le caoutchouc.
- Repenser le stockage:Conservez les aliments et les friandises pour chiens dans des contenants hermétiques en verre ou en acier inoxydable plutôt que de les laisser dans leur emballage en plastique d’origine.
- Inspectez votre maison:Limitez l’accès de votre chien aux objets en plastique de mauvaise qualité qui pourraient être mâchés ou ingérés.
- Évitez de chauffer les plastiques:Ne mettez jamais d’aliments ou de friandises au micro-ondes dans des récipients en plastique, car la chaleur augmente la lixiviation des produits chimiques.
Plaidoyer pour des normes plus sûres
Au-delà des choix personnels, les propriétaires d’animaux peuvent plaider en faveur de meilleures normes de sécurité dans le secteur des produits pour animaux de compagnie. Soutenir les marques qui privilégient les matériaux non toxiques et les pratiques durables envoie un message puissant. De plus, rester informé des rappels de produits ou des recherches émergentes peut aider à protéger votre chien des risques cachés.
La vue d’ensemble
Bien que le plastique soit omniprésent dans la vie moderne, ses effets potentiels sur la santé ne peuvent être ignorés. Pour nos chiens, réduire l’exposition aux plastiques nocifs est un moyen simple mais efficace de soutenir leur santé et leur bien-être à long terme. En faisant des choix conscients et en sensibilisant les gens, nous pouvons faire en sorte que nos animaux de compagnie vivent une vie plus heureuse et plus saine.

par TCMVET | 11 décembre 2024 | Cancer et tumeurs du chien
En ce qui concerne les chiens, la taille a son importance, mais pas seulement de la manière dont on le pense habituellement. Alors que les grands chiens sont admirés pour leur force et les petits pour leur charme, des études récentes ont révélé un lien surprenant entre la taille d'un chien et son risque de développer un cancer. Plongeons-nous dans ce lien intriguant et découvrons ce qu'il signifie pour les propriétaires d'animaux de compagnie.
La science derrière la taille et le risque de cancer
Des études ont montré que les grandes races, comme les Dogues allemands, les Bouviers bernois et les Rottweilers, sont plus sujettes à certains cancers que leurs homologues plus petits. Mais pourquoi ? La réponse se trouve dans la biologie. Les grands chiens grandissent plus vite et ont plus de cellules dans leur corps. Cette activité cellulaire accrue augmente les risques de mutations, qui peuvent conduire au cancer.
En revanche, les petites races comme les chihuahuas et les teckels ont tendance à avoir un risque de cancer plus faible, mais ne sont pas complètement immunisées. Certains cancers, comme les tumeurs des mastocytes, peuvent néanmoins toucher les chiens de petite taille, souvent en raison de prédispositions génétiques plutôt que de la taille.
Croissance rapide : une arme à double tranchant
Les grandes races connaissent des poussées de croissance rapides pendant leur enfance, ce qui met leur corps à rude épreuve. Cette croissance rapide peut entraîner une division cellulaire moins stable, ce qui augmente le risque de comportement cellulaire anormal au fil du temps. De plus, les exigences métaboliques des chiens de grande taille peuvent accélérer le vieillissement, les rendant plus vulnérables aux maladies, notamment au cancer, à mesure qu'ils vieillissent.
Longévité et risque de cancer
Les petits chiens vivent souvent beaucoup plus longtemps que les grandes races. Si cette longévité donne aux petits chiens plus de temps pour développer des maladies liées à l’âge, elle signifie également que leur croissance et leur renouvellement cellulaire plus lents peuvent les protéger des cancers à apparition précoce, généralement observés chez les grandes races. En revanche, la durée de vie plus courte des grands chiens est souvent corrélée à une prévalence plus élevée de cancers agressifs à un plus jeune âge.
Ce que les propriétaires d’animaux peuvent faire
Les propriétaires d'animaux peuvent prendre des mesures proactives pour minimiser les risques de cancer, quelle que soit la taille de leur chien. Des contrôles vétérinaires réguliers, une alimentation équilibrée et des routines d'exercice appropriées sont essentiels. Pour les grandes races, une attention particulière doit être accordée au maintien d'un poids santé, car l'obésité peut aggraver les risques de cancer. Les petits chiens, bien que moins sujets aux cancers liés à la taille, bénéficient toujours de dépistages génétiques pour identifier les risques héréditaires à un stade précoce.
Redéfinir « La taille compte »
Le lien entre la taille et le risque de cancer nous pousse à repenser notre approche des soins aux chiens. Bien que nous ne puissions pas modifier la taille d'un chien, comprendre comment elle influence sa santé peut nous aider à prendre des décisions éclairées. Du choix des races à l'adaptation des routines de soins, ces connaissances permettent aux propriétaires d'animaux de compagnie de donner à leurs amis à quatre pattes les meilleures chances de vivre une vie longue et saine.
En fin de compte, qu’il soit grand ou petit, chaque chien mérite de l’amour, de l’attention et des soins de santé proactifs. En restant informés, nous pouvons tous jouer un rôle dans la réduction des risques de cancer et assurer le bien-être de nos compagnons canins.






