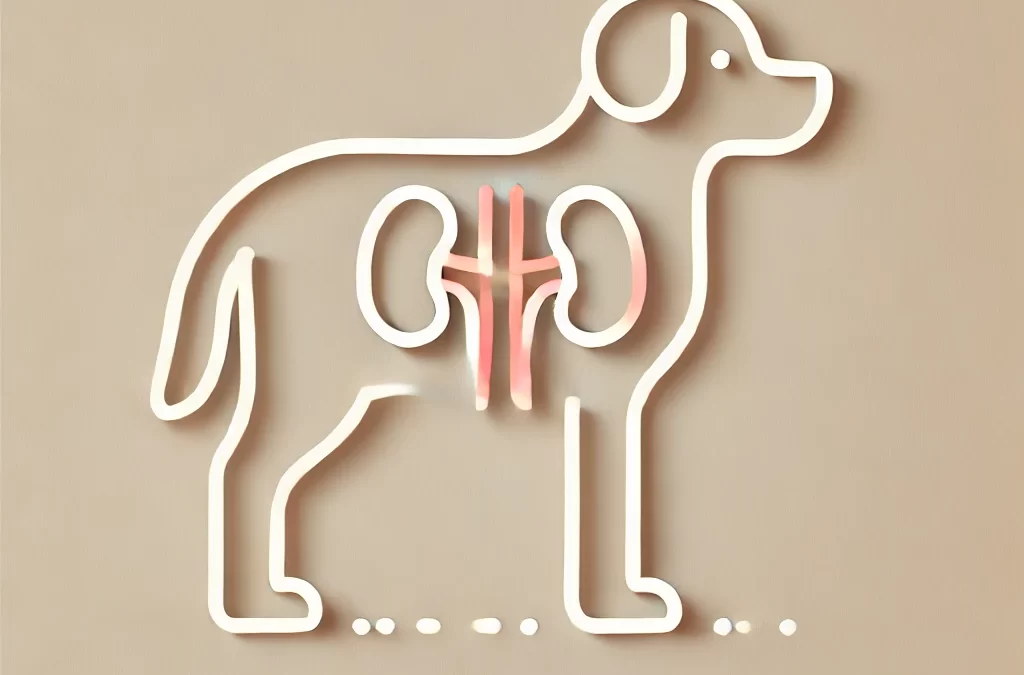
por TCMVET | 12 de diciembre de 2024 | Cáncer y tumores en perros
El cáncer de riñón en perros es relativamente poco frecuente, pero puede afectar significativamente la salud del perro cuando se presenta. Los síntomas suelen aparecer de forma gradual, lo que dificulta la detección temprana. Conocer los posibles signos puede ayudar a los dueños de mascotas a buscar atención veterinaria oportuna.
Síntomas comunes del cáncer de riñón en perros
- Aumento de la sed y la micción (polidipsia y poliuria):
- Beber y orinar en exceso pueden indicar una función renal deteriorada debido al tumor.
- Loss of Appetite:
- Los perros con cáncer de riñón a menudo experimentan una disminución del apetito, lo que conduce a una pérdida de peso.
- Weight Loss:
- Incluso con una ingesta normal de alimentos, puede producirse pérdida de peso a medida que el cuerpo gasta energía combatiendo la enfermedad.
- Vómitos y náuseas:
- La disfunción renal causada por el cáncer puede provocar la acumulación de toxinas en la sangre, causando problemas gastrointestinales.
- Dolor o hinchazón abdominal:
- Los tumores pueden causar hinchazón visible o molestias al tocar el abdomen.
- Sangre en la orina (hematuria):
- La orina puede verse rosada o roja debido al sangrado del tumor.
- Lethargy:
- Los perros con cáncer de riñón pueden presentar niveles de energía reducidos y renuencia a participar en actividades normales.
- Difficulty Breathing:
- En casos avanzados, los tumores pueden presionar los órganos circundantes y causar problemas respiratorios.
- Encías pálidas:
- La anemia, a menudo asociada con el cáncer de riñón, puede provocar que las encías se vean pálidas.
- Mal aliento (aliento urémico):
- La acumulación de toxinas en la sangre debido a una función renal reducida puede provocar un olor parecido al amoníaco.
Cuándo acudir al veterinario
Si su perro presenta una combinación de estos síntomas, es fundamental que busque atención veterinaria de inmediato. Si bien estos signos no son exclusivos del cáncer de riñón, a menudo indican un problema de salud subyacente grave que requiere diagnóstico y tratamiento.
Diagnóstico del cáncer de riñón en perros
Un veterinario normalmente utilizará los siguientes métodos para confirmar el cáncer de riñón:
- Examen físico: Para detectar hinchazón o malestar.
- Análisis de orina: Para comprobar si hay sangre o sustancias anormales en la orina.
- Análisis de sangre: Para evaluar la función renal y detectar cualquier anomalía.
- Imágenes: La ecografía, las radiografías o las tomografías computarizadas pueden identificar tumores y su extensión.
- Biopsia: Se puede tomar una muestra del tumor para confirmar su naturaleza.
Tratamiento y pronóstico
Las opciones de tratamiento dependen del tipo y estadio del tumor, pero pueden incluir:
- Cirugía: Extirpación del riñón afectado (nefrectomía) si el cáncer está localizado.
- Quimioterapia: Para ciertos tipos de cáncer, la quimioterapia puede retardar la progresión.
- Cuidados de apoyo: Manejo del dolor, hidratación y apoyo nutricional para mantener la calidad de vida.
La detección temprana mejora los resultados del tratamiento, por lo que los controles veterinarios regulares son vitales, especialmente para los perros mayores.
Al reconocer estos síntomas y actuar rápidamente, puede brindarle a su perro la mejor posibilidad de recibir atención eficaz y mantener una buena calidad de vida.
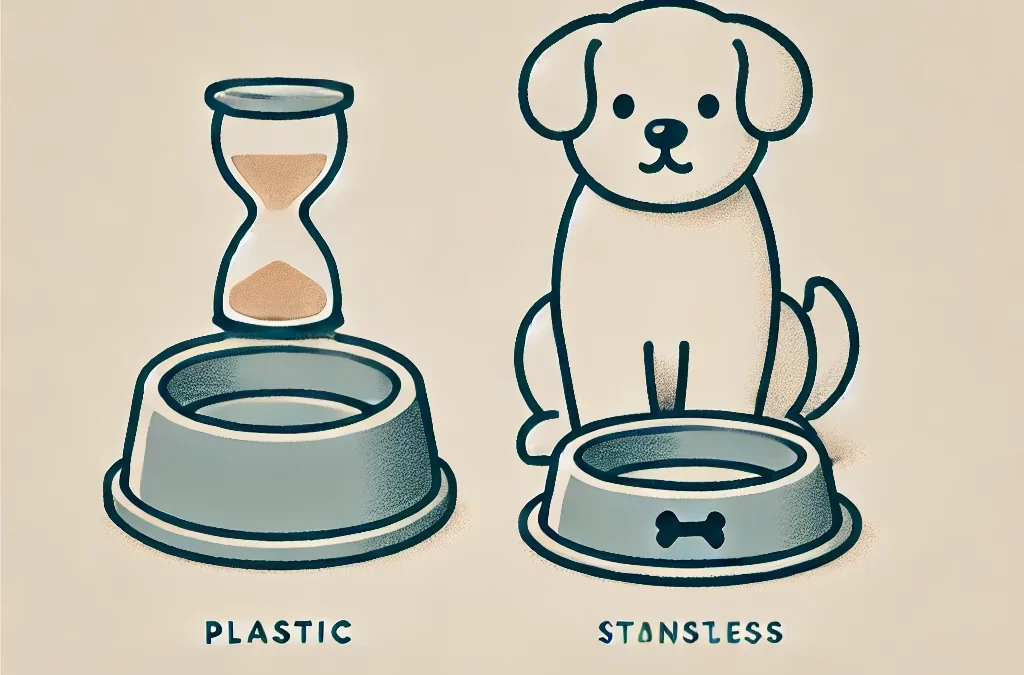
por TCMVET | 11 de diciembre de 2024 | Cáncer y tumores en perros
El plástico está presente en todas partes en nuestra vida diaria, desde los envases de alimentos hasta los artículos del hogar e incluso en productos diseñados para nuestros amigos peludos. Pero, ¿podría este material aparentemente inocuo representar una amenaza para la salud de nuestros perros? Estudios recientes sugieren que la exposición prolongada a ciertos tipos de plástico podría aumentar el riesgo de cáncer en los perros. Exploremos la ciencia y lo que los dueños de mascotas pueden hacer para proteger a sus mascotas.
Los peligros ocultos de los plásticos
Muchos tipos de plásticos contienen sustancias químicas nocivas, como el bisfenol A (BPA), los ftalatos y el cloruro de polivinilo (PVC). Estas sustancias químicas se utilizan a menudo para que el plástico sea duradero, flexible o transparente. Sin embargo, pueden filtrarse en los alimentos, el agua o incluso el medio ambiente, especialmente cuando los plásticos se calientan, se rayan o se degradan.
En los animales, estas sustancias químicas pueden actuar como disruptores endocrinos, interfiriendo en la función hormonal. La exposición prolongada puede provocar cambios celulares, estrés oxidativo e incluso la formación de tumores, lo que aumenta la probabilidad de cáncer. En el caso de los perros, cuyos hábitos diarios suelen incluir masticar, lamer y el contacto cercano con diversos materiales, los riesgos son mayores.
Fuentes cotidianas de exposición al plástico para los perros
- Cuencos de comida y agua:Muchos dueños de perros utilizan, sin saberlo, cuencos de plástico, que pueden liberar sustancias nocivas, especialmente si se rayan o se exponen a la luz solar.
- Juguetes para masticar:Los juguetes de plástico de baja calidad a menudo contienen materiales no regulados que pueden suponer un riesgo si se ingieren o se mastican excesivamente.
- Embalaje:Las golosinas, croquetas y otros productos para perros a menudo se almacenan en envases de plástico, que pueden filtrar sustancias químicas en los alimentos.
- Artículos para el hogar:Los perros entran frecuentemente en contacto con objetos de plástico en la casa, desde contenedores hasta muebles.
Riesgos de cáncer relacionados con el plástico
Si bien los vínculos directos entre la exposición al plástico y el cáncer en perros aún se encuentran en estudio, la evidencia de investigaciones en humanos y animales indica una relación preocupante. En los perros, los cánceres como los tumores mamarios, el cáncer testicular y el linfoma pueden verse influenciados por toxinas ambientales, incluidas las que se encuentran en el plástico. Las razas más pequeñas o los perros con problemas de salud preexistentes pueden ser especialmente vulnerables.
Medidas para reducir la exposición al plástico
Los dueños de mascotas pueden tomar medidas proactivas para minimizar la exposición de sus perros a plásticos dañinos:
- Cambie a tazones más seguros:Utilice recipientes de acero inoxidable, cerámica o vidrio para alimentos y agua en lugar de recipientes de plástico.
- Elija juguetes de alta calidad:Opte por juguetes no tóxicos, libres de BPA o fabricados con materiales naturales como el caucho.
- Repensar el almacenamiento:Guarde la comida y las golosinas para perros en recipientes herméticos hechos de vidrio o acero inoxidable en lugar de dejarlos en su embalaje de plástico original.
- Inspeccione su hogar:Limite el acceso de su perro a artículos de plástico de baja calidad que puedan ser masticados o ingeridos.
- Evite calentar plásticos:Nunca caliente en microondas alimentos o golosinas en recipientes de plástico, ya que el calor aumenta la lixiviación de sustancias químicas.
Abogando por estándares más seguros
Más allá de las decisiones personales, los dueños de mascotas pueden abogar por mejores estándares de seguridad en la industria de productos para mascotas. Apoyar a las marcas que priorizan los materiales no tóxicos y las prácticas sostenibles envía un mensaje poderoso. Además, mantenerse informado sobre los retiros de productos o las investigaciones emergentes puede ayudar a proteger a su perro de riesgos ocultos.
El panorama más amplio
Si bien el plástico es una parte omnipresente de la vida moderna, no se pueden ignorar sus posibles efectos sobre la salud. Para nuestros perros, reducir la exposición a plásticos nocivos es una forma sencilla pero eficaz de contribuir a su salud y bienestar a largo plazo. Al tomar decisiones conscientes y difundir la conciencia, podemos garantizar que nuestras mascotas vivan vidas más felices y saludables.

por TCMVET | 11 de diciembre de 2024 | Cáncer y tumores en perros
En el caso de los perros, el tamaño sí importa, pero no solo en la forma en que solemos pensar. Si bien los perros grandes son admirados por su fuerza y los pequeños por su encanto, estudios recientes han descubierto una sorprendente conexión entre el tamaño de un perro y su riesgo de desarrollar cáncer. Profundicemos en este intrigante vínculo y exploremos lo que significa para los dueños de mascotas.
La ciencia detrás del tamaño y el riesgo de cáncer
Los estudios han demostrado que las razas más grandes, como el gran danés, el boyero de Berna y el rottweiler, son más propensas a ciertos tipos de cáncer en comparación con sus contrapartes más pequeñas. Pero, ¿por qué? La respuesta está en la biología. Los perros grandes crecen más rápido y tienen más células en sus cuerpos. Esta mayor actividad celular aumenta las probabilidades de mutaciones, que pueden provocar cáncer.
Por otro lado, las razas pequeñas, como los chihuahuas y los teckels, tienden a tener un menor riesgo de cáncer, pero no son completamente inmunes. Ciertos tipos de cáncer, como los tumores de mastocitos, pueden afectar a los perros más pequeños, a menudo debido a predisposiciones genéticas más que al tamaño.
Crecimiento rápido: un arma de doble filo
Las razas grandes experimentan períodos de crecimiento rápido durante la etapa de cachorro, lo que supone una enorme tensión para sus cuerpos. Este crecimiento rápido puede dar lugar a una división celular menos estable, lo que aumenta el riesgo de un comportamiento celular anormal con el tiempo. Además, las demandas metabólicas de los perros más grandes pueden acelerar el envejecimiento, haciéndolos más susceptibles a enfermedades, incluido el cáncer, a medida que envejecen.
Longevidad y riesgo de cáncer
Los perros pequeños suelen vivir mucho más que las razas grandes. Si bien esta longevidad les da más tiempo para desarrollar enfermedades relacionadas con la edad, también significa que su crecimiento y renovación celular más lentos pueden protegerlos de los cánceres de aparición temprana que se observan comúnmente en las razas más grandes. Por el contrario, la menor esperanza de vida de los perros más grandes suele correlacionarse con una mayor prevalencia de cánceres agresivos a una edad más temprana.
Qué pueden hacer los dueños de mascotas
Los dueños de mascotas pueden tomar medidas proactivas para minimizar los riesgos de cáncer, independientemente del tamaño de su perro. Los controles veterinarios regulares, las dietas equilibradas y las rutinas de ejercicio adecuadas son esenciales. En el caso de las razas grandes, se debe prestar especial atención a mantener un peso saludable, ya que la obesidad puede exacerbar aún más los riesgos de cáncer. Los perros pequeños, aunque son menos propensos a los cánceres relacionados con el tamaño, igualmente se benefician de las pruebas genéticas para identificar los riesgos hereditarios de forma temprana.
Redefiniendo el concepto de “El tamaño importa”
El vínculo entre el tamaño y el riesgo de cáncer nos desafía a repensar nuestro enfoque en el cuidado de los perros. Si bien no podemos cambiar el tamaño de un perro, comprender cómo influye en su salud puede ayudarnos a tomar decisiones informadas. Desde la elección de razas hasta la personalización de rutinas de cuidado, este conocimiento permite a los dueños de mascotas brindarles a sus amigos peludos la mejor oportunidad de tener una vida larga y saludable.
Al final, ya sean grandes o pequeños, todos los perros merecen amor, atención y un cuidado de salud proactivo. Si nos mantenemos informados, todos podemos contribuir a reducir los riesgos de cáncer y garantizar que nuestros compañeros caninos prosperen.

por TCMVET | 9 de diciembre de 2024 | Cáncer y tumores en perros
Los tumores de la columna vertebral en perros, aunque son poco frecuentes, pueden afectar gravemente su movilidad y calidad de vida. Estos tumores pueden desarrollarse dentro o alrededor de la columna vertebral, lo que afecta el funcionamiento del sistema nervioso. La detección temprana y el tratamiento adecuado son esenciales para brindar la mejor atención a su amigo peludo. Aquí encontrará una guía completa sobre los tipos de tumores de la columna vertebral en perros y sus síntomas, causas y opciones de tratamiento.
Tipos comunes de tumores espinales en perros
- Tumores intramedulares
- Descripción: Estos tumores se originan en la propia médula espinal y suelen surgir de las células gliales, que sostienen el sistema nervioso.
- Ejemplos: Astrocitomas, ependimomas y oligodendrogliomas
- Síntomas: Debilidad gradual, descoordinación y posible parálisis en casos graves.
- Tratamiento: Cirugía (si es posible), radioterapia y cuidados de apoyo.
- Tumores extradurales
- Descripción: Estos tumores aparecen fuera de la médula espinal pero dentro del canal espinal, a menudo comprimiendo la médula y causando problemas neurológicos.
- Ejemplos: Osteosarcomas, fibrosarcomas y linfomas
- Síntomas: Dolor de espalda, dificultad para caminar y debilidad muscular.
- Tratamiento: Extirpación quirúrgica, quimioterapia o radiación, según el tipo de tumor.
- Tumores intradurales y extramedulares
- Descripción: Ubicados dentro del canal espinal pero fuera de la médula espinal, estos tumores crecen en las meninges o raíces nerviosas circundantes.
- Ejemplos: Meningiomas, tumores de la vaina nerviosa (schwannomas)
- Síntomas: Dolor, falta de coordinación y posible incontinencia urinaria o intestinal.
- Tratamiento: Cirugía y radioterapia
- Tumores vertebrales
- Descripción: Estos tumores surgen de los huesos de la columna vertebral, provocando inestabilidad estructural y posible compresión de la médula espinal.
- Ejemplos: Osteosarcoma, condrosarcoma
- Síntomas: Dolor intenso, hinchazón y dificultad para estar de pie o caminar.
- Tratamiento: Cirugía, quimioterapia y manejo del dolor.
Symptoms of Spinal Tumors in Dogs
Los síntomas de los tumores espinales pueden variar según la ubicación y el tamaño del tumor, pero los signos comunes incluyen:
- Renuencia a moverse o jugar
- Dificultad para caminar o arrastrar extremidades
- Dolor o sensibilidad en la espalda o el cuello.
- Pérdida del control de la vejiga o los intestinos
- Cambios repentinos en el comportamiento o la postura.
Causas y factores de riesgo
Los tumores espinales en perros pueden ser causados por:
- Predisposición genética: Ciertas razas como los pastores alemanes y los golden retrievers pueden tener mayor riesgo.
- Age: Los perros mayores tienen más probabilidades de desarrollar tumores espinales.
- Metástasis del cáncer: Los tumores de otras partes del cuerpo pueden propagarse a la columna vertebral.
Diagnóstico y tratamiento
Los veterinarios utilizan varios métodos para diagnosticar tumores espinales:
- Examen neurológico: Evalúa los reflejos, la coordinación y la respuesta al dolor.
- Imágenes: Radiografías, resonancias magnéticas o tomografías computarizadas para localizar y evaluar el tumor.
- Biopsia: Confirma el tipo de tumor para un tratamiento específico.
Las opciones de tratamiento incluyen:
- Cirugía: El método preferido para tumores accesibles y operables.
- Radioterapia: Se utiliza para tumores inoperables o residuales postoperatorios.
- Quimioterapia: Eficaz para algunos tumores espinales metastásicos o primarios.
- Tratamiento del dolor: Imprescindible para mejorar la calidad de vida del perro.
Cómo apoyar la recuperación de su perro
El cuidado de los perros con tumores espinales debe incluir:
- Proporcionar una cama suave y de apoyo para prevenir las úlceras por presión.
- Ayudar con la movilidad mediante arneses o carros.
- Mantener una dieta nutritiva para favorecer la salud general
- Seguimiento regular con el veterinario para monitorear la evolución.
Conclusión
Los tumores de la columna vertebral en perros requieren atención inmediata y cuidados especializados. Si bien el pronóstico depende del tipo de tumor y su progresión, los avances en medicina veterinaria han hecho que los tratamientos sean más efectivos. Si comprende los síntomas y las opciones disponibles, puede asegurarse de que su perro reciba la mejor atención y apoyo.

por TCMVET | 9 de diciembre de 2024 | Cáncer y tumores en perros
La salud de la piel de los perros suele ser un reflejo de su bienestar general, aunque algunas afecciones pueden resultar desconcertantes incluso para los dueños de mascotas más atentos. Una de esas afecciones poco frecuentes es epiteliomas cornificantes, un tipo de tumor benigno de la piel que puede causar preocupación por su apariencia y efectos. Profundicemos en esta inusual afección dermatológica, sus causas, tratamientos y lo que la convierte en un desafío único en la atención médica canina.
¿Qué son los epiteliomas cornificantes?
Los epiteliomas cornificantes son tumores benignos que se originan en las glándulas sebáceas, específicamente en el epitelio (células de la piel) responsable de la producción de queratina. Estos tumores suelen presentarse como crecimientos nodulares similares a verrugas en la piel del perro. Si bien no son potencialmente mortales, su potencial para causar molestias o infecciones significa que no deben ignorarse.
¿Qué causa los epiteliomas cornificantes?
La causa exacta de los epiteliomas cornificantes no se comprende por completo, pero los factores que contribuyen pueden incluir:
- Predisposición genética: Razas como los Cocker Spaniels, Beagles y Siberian Huskies son más propensas a desarrollar estos crecimientos.
- Desequilibrios hormonales: La actividad de las glándulas sebáceas puede verse influenciada por cambios hormonales, particularmente en perros mayores.
- Deficiencias dietéticas: Una mala nutrición puede provocar desequilibrios en la salud de la piel, agravando potencialmente enfermedades como los epiteliomas.
Reconocer los síntomas
Los epiteliomas cornificantes suelen aparecer como:
- Nódulos pequeños y firmes con una textura similar a una verruga.
- De color amarillento o ceroso debido a la acumulación de queratina.
- Se localiza alrededor de la cabeza, el cuello o la espalda, pero puede aparecer en cualquier parte.
- Ocasionalmente se acompaña de enrojecimiento o inflamación si ocurre una infección secundaria.
Si bien estos crecimientos son benignos, los cambios rápidos en tamaño, color o textura deben ser evaluados por un veterinario para descartar neoplasias malignas.
Diagnóstico de los epiteliomas cornificantes
El diagnóstico generalmente implica:
- Examen físico: Un veterinario evaluará el tamaño, la ubicación y la apariencia de los crecimientos.
- Aspiración con aguja fina (AAF): Se extrae una muestra de células y se analiza para confirmar la naturaleza del tumor.
- Biopsia: En algunos casos, puede ser necesaria una biopsia para diferenciar entre epiteliomas benignos y otras afecciones o cánceres de la piel.
Opciones de tratamiento
El tratamiento depende de la gravedad y el impacto de los epiteliomas en la calidad de vida de su perro.
- Supervisión
En el caso de crecimientos pequeños y no problemáticos, suele ser suficiente un seguimiento regular.
- Asegúrese de que el área permanezca limpia y libre de infecciones.
- Utilice tratamientos tópicos calmantes si lo recomienda su veterinario.
- Extirpación quirúrgica
Si los crecimientos causan molestias, infecciones recurrentes o problemas estéticos, la extirpación quirúrgica es una solución común.
- Las técnicas mínimamente invasivas como la cirugía láser pueden reducir el tiempo de recuperación.
- Terapias tópicas o sistémicas
- Los retinoides o los suplementos de vitamina A pueden regular la producción de queratina.
- Se pueden recetar antibióticos para infecciones bacterianas secundarias.
Enfoques innovadores y naturales
Para propietarios que buscan complementar los tratamientos convencionales con atención holística:
- Ácidos grasos omega-3: Estos pueden reducir la inflamación y promover la salud general de la piel.
- Remedios de hierbas: La caléndula y el aloe vera pueden aliviar las zonas irritadas.
- Ajustes dietéticos: Una dieta rica en antioxidantes y proteínas de alta calidad favorece la regeneración de la piel.
Medidas preventivas
Aunque no todos los casos de epiteliomas cornificantes se pueden prevenir, estas medidas pueden ayudar a mantener una salud óptima de la piel:
- Aseo regular: Mantiene la piel limpia y favorece la detección temprana de anomalías.
- Dieta equilibrada: Apoya el sistema inmunológico y reduce la probabilidad de problemas en la piel.
- Visitas veterinarias de rutina: La intervención temprana es clave para controlar cualquier afección de la piel.
Un desafío único en la dermatología canina
Los epiteliomas cornificantes resaltan la importancia de comprender y abordar incluso las afecciones poco frecuentes en los perros. Si bien son benignos, estos crecimientos pueden afectar la comodidad y la apariencia de su mascota, por lo que es esencial un tratamiento rápido y eficaz. Si se mantiene informado y trabaja en estrecha colaboración con su veterinario, puede asegurarse de que su perro se mantenga saludable, feliz y próspero.





