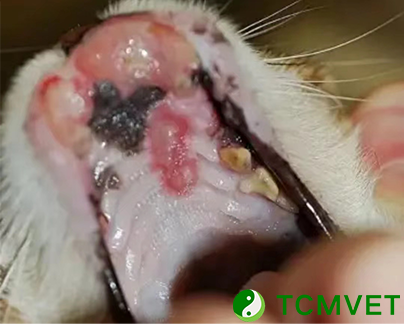
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) is a prevalent type of cancer in small animals, particularly affecting dogs and cats. It’s a malignant tumor that originates in the squamous epithelium, which is the outermost layer of the skin, as well as in the linings of the organs and cavities of the body. As a pet owner or a veterinary enthusiast, understanding the treatment options available for SCC in small animals is crucial for managing this disease effectively.
1. Surgical Removal:
Surgery is often the primary treatment for squamous cell carcinoma, particularly when the tumor is localized and has not metastasized. The goal of the surgery is to completely remove the cancerous tissue. In cases where SCC is located in the skin, the surgical removal is relatively straightforward. However, if the tumor is in more complex areas, such as the mouth or near the nail beds, the procedure can be more challenging. Post-surgical histopathology is essential to ensure that the margins are clear of cancer cells.
2. Radiation Therapy:
Radiation therapy is another effective treatment, particularly for tumors that are difficult to remove surgically, such as those in the oral cavity. It involves the use of high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors. This therapy is often used post-surgery if the margins are not clear or if the cancer is inoperable. For some pets, radiation therapy can be used as a palliative treatment to relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life.
3. Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy is less commonly used in treating SCC in small animals compared to other types of cancer, but it may be recommended in cases where the cancer has metastasized. It involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or slow their growth. Chemotherapy can be administered orally or through injections and often comes with side effects such as nausea, fatigue, and increased susceptibility to infections.
4. Cryosurgery:
For smaller or superficial SCC lesions, cryosurgery might be an option. This treatment involves using extreme cold (liquid nitrogen) to freeze and destroy abnormal cells. It is less invasive than traditional surgery and is usually performed on an outpatient basis.
5. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT):
PDT is a relatively new treatment option that involves using drugs, known as photosensitizing agents, alongside light to kill cancer cells. The drug is absorbed by the cancer cells and, when exposed to a specific wavelength of light, it produces a form of oxygen that kills the cells.
6. Electrochemotherapy:
Electrochemotherapy combines chemotherapy and electric pulses to enhance the absorption of chemotherapeutic drugs by the cancer cells. This treatment is gaining interest for treating tumors that are difficult to treat with conventional methods.
7. Palliative Care:
In cases where the cancer is too advanced, or the animal is not a good candidate for aggressive treatments, palliative care becomes the focus. This involves managing symptoms and maintaining the quality of life with medications, nutritional support, and pain management.
Treatment for squamous cell carcinoma in small animals varies based on the tumor’s location, size, and the general health of the animal. Advances in veterinary medicine have significantly increased the effectiveness of SCC treatments, offering hope and improved outcomes for pets diagnosed with this condition. Regular check-ups and early detection remain key in successfully managing and treating SCC. As always, consultation with a qualified veterinary oncologist is crucial to determine the best course of action for each individual case.