
by TCMVET | Jul 4, 2024 | Dog Cancer & Tumors
Canine bone cancer, also known as osteosarcoma, is a formidable adversary for our furry companions. As pet owners, understanding the implications of this disease is crucial, especially when it comes to the potential for paralysis. This article delves into the intricacies of canine bone cancer, its symptoms, treatment options, and how it can lead to paralysis, providing valuable insights for pet owners seeking to protect their beloved pets.
Understanding Canine Bone Cancer
Osteosarcoma is the most common type of bone cancer in dogs, predominantly affecting large and giant breeds. This aggressive cancer originates in the bone, leading to pain, swelling, and ultimately, the destruction of the bone itself. Early detection is vital for effective treatment, yet the symptoms can often be mistaken for less severe conditions like arthritis or minor injuries.
Symptoms to Watch For
Recognizing the early signs of osteosarcoma can make a significant difference in your dog’s prognosis. Common symptoms include:
- Lameness: Persistent limping or difficulty walking is often one of the first signs.
- Swelling: Noticeable swelling at the site of the tumor, typically around the limbs.
- Pain: Your dog may show signs of discomfort or pain when touched or when using the affected limb.
- Fatigue: Reduced activity levels and reluctance to play or exercise.
- Weight Loss: Unexplained weight loss despite normal eating habits.
The Link Between Bone Cancer and Paralysis
One of the most devastating complications of canine bone cancer is the potential for paralysis. As the tumor grows, it can exert pressure on surrounding tissues, including nerves. If the cancer spreads to the spine or affects the spinal cord, it can lead to partial or complete paralysis. This progression underscores the importance of early detection and intervention.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing osteosarcoma typically involves a combination of physical examinations, X-rays, and biopsies. Once confirmed, treatment options may include:
- Surgery: Amputation of the affected limb is often recommended to remove the primary tumor and alleviate pain.
- Chemotherapy: To address metastasis and improve survival rates, chemotherapy is often administered alongside surgery.
- Radiation Therapy: This can be used to manage pain and reduce tumor size, particularly in cases where surgery is not feasible.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
In addition to conventional treatments, many pet owners explore alternative therapies to support their dog’s health. These may include:
- CBD Oil: Known for its anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving properties, CBD oil is increasingly used to manage cancer symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Dietary Supplements: Supplements like Omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants can support overall health and strengthen the immune system.
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercises and therapies can help maintain mobility and muscle strength, reducing the risk of paralysis.
Preventive Measures and Regular Check-ups
While osteosarcoma cannot always be prevented, regular veterinary check-ups and a healthy lifestyle can play a significant role in early detection and management. Maintaining an active lifestyle, providing a balanced diet, and monitoring any changes in your dog’s behavior or physical condition are essential steps in safeguarding their health.
Canine bone cancer is a challenging diagnosis, but understanding its implications, especially the threat of paralysis, empowers pet owners to take proactive measures. Early detection, combined with a comprehensive treatment plan, can significantly improve your dog’s quality of life and potentially extend their time with you. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and cherish every moment with your loyal companion.

by TCMVET | Jul 3, 2024 | Dog Cancer & Tumors
When we think about canine cancer, the focus often falls on tumors and their direct effects. However, the impact of cancer on a dog’s balance and coordination is a crucial aspect that can significantly affect their quality of life. This article explores how cancer affects these critical functions and what pet owners can do to help their furry friends navigate these challenges.
The Connection Between Canine Cancer and Balance Issues
1. Brain Tumors and Neurological Effects
Brain tumors are a primary cause of balance and coordination issues in dogs. These tumors can interfere with the brain’s normal functions, including those that control movement and balance. Symptoms might include:
- Head Tilt: A noticeable tilt of the head to one side.
- Circling: Walking in circles rather than a straight line.
- Stumbling and Falling: Difficulty maintaining balance, leading to frequent falls.
- Seizures: Uncontrolled movements that can affect overall coordination.
2. Inner Ear Tumors
The inner ear plays a vital role in maintaining balance. Tumors in this area can disrupt the vestibular system, leading to:
- Dizziness: Dogs may appear disoriented and unsteady.
- Nystagmus: Rapid, involuntary eye movements.
- Loss of Coordination: Difficulty walking or standing normally.
3. Metastatic Cancer
Cancer that spreads from its original site to other parts of the body can also affect balance and coordination. For example, cancer that metastasizes to the spine can compress the spinal cord, impacting a dog’s ability to walk and maintain balance.
Symptoms to Watch For
Early detection is key to managing balance and coordination issues in dogs with cancer. Symptoms to monitor include:
- Unsteady Gait: Walking with a wobble or unsteady steps.
- Lack of Coordination: Difficulty performing routine movements.
- Reluctance to Move: Avoiding physical activity due to discomfort or instability.
- Frequent Falls: Tripping or falling more often than usual.
- Eye and Head Movements: Abnormal eye movements or head tilting.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Proper diagnosis and timely intervention can help manage the impact of cancer on your dog’s balance and coordination. Veterinary care may include:
1. Neurological Examination
A comprehensive neurological exam can help identify the underlying cause of balance issues. This may involve:
- Reflex Tests: Checking limb reflexes and responses.
- Eye Movement Assessment: Observing for nystagmus or abnormal eye movements.
- Gait Analysis: Evaluating walking patterns and coordination.
2. Imaging Techniques
Advanced imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans can detect tumors in the brain, inner ear, or spine, providing a clear picture of the affected areas.
3. Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type and location of the cancer. Options may include:
- Surgery: Removing tumors that are accessible and operable.
- Radiation Therapy: Targeting tumors with radiation to shrink them and alleviate symptoms.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to slow tumor growth and spread.
- Supportive Care: Medications to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Supporting Your Dog at Home
Helping your dog cope with balance and coordination issues involves making some adjustments at home:
1. Safe Environment
Ensure your home is free from obstacles that could cause your dog to trip or fall. Use non-slip mats and remove clutter from pathways.
2. Assistive Devices
Consider using harnesses or support slings to help your dog move around safely.
3. Gentle Exercise
Encourage gentle exercise to maintain muscle strength and coordination, but avoid activities that could cause falls or injuries.
4. Regular Veterinary Visits
Keep up with regular veterinary check-ups to monitor your dog’s condition and adjust treatments as necessary.
Canine cancer can significantly impact a dog’s balance and coordination, but with early detection, appropriate treatment, and supportive care, you can help your furry friend navigate these challenges. By staying vigilant and proactive, you can ensure your dog maintains the best possible quality of life.

by TCMVET | Jul 3, 2024 | Dog Cancer & Tumors
Understanding the intricate relationship between canine cancer and blood sugar levels is vital for pet owners and veterinarians. Recent studies suggest that managing blood sugar levels can play a crucial role in the treatment and prevention of cancer in dogs. This article delves into the connection between cancer and blood sugar, highlighting key insights and practical steps for maintaining your dog’s health.
How Blood Sugar Levels Affect Canine Cancer
1. The Role of Glucose in Cancer Growth
Cancer cells thrive on glucose, using it as a primary energy source to fuel their rapid growth and proliferation. Elevated blood sugar levels can create an environment that supports the development and spread of cancer. By understanding this connection, pet owners can take proactive steps to regulate their dog’s blood sugar, potentially slowing cancer progression.
2. Insulin Resistance and Cancer Risk
Just like in humans, insulin resistance in dogs can lead to elevated blood sugar levels. Insulin resistance occurs when cells become less responsive to insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar. This condition not only increases the risk of diabetes but also creates a favorable environment for cancer cells to grow. Monitoring and managing insulin resistance is, therefore, a crucial aspect of cancer prevention and treatment in dogs.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the symptoms of blood sugar imbalances and cancer in dogs is essential for early detection and intervention. Common signs include:
- Increased Thirst and Urination: These can indicate high blood sugar levels.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Despite eating well, weight loss can signal diabetes or cancer.
- Lethargy: Low energy levels can be a symptom of both high blood sugar and cancer.
- Frequent Infections: High blood sugar can weaken the immune system, making dogs more susceptible to infections.
- Visible Tumors or Lumps: Physical signs of cancer that require immediate veterinary attention.
To diagnose these conditions, veterinarians may perform blood tests, glucose tolerance tests, and biopsies to identify the underlying issues and develop a treatment plan.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels in Dogs with Cancer
1. Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet low in simple sugars and high in protein and fiber can help regulate blood sugar levels. Foods with a low glycemic index release glucose slowly, preventing spikes in blood sugar. Consider incorporating these elements into your dog’s diet:
- Lean Proteins: Chicken, turkey, and fish
- Fiber-Rich Vegetables: Green beans, carrots, and pumpkin
- Whole Grains: Brown rice and oats
Consult with your veterinarian to create a tailored nutrition plan that meets your dog’s specific needs.
2. Regular Exercise
Physical activity helps regulate blood sugar levels and maintain a healthy weight, reducing the risk of both diabetes and cancer. Engage your dog in regular walks, play sessions, and activities that keep them active and fit.
3. Medications and Supplements
In some cases, veterinarians may prescribe medications to manage blood sugar levels or recommend supplements that support metabolic health. These can include:
- Insulin: For dogs diagnosed with diabetes
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: To support overall health and reduce inflammation
- Antioxidants: To combat oxidative stress and support the immune system
4. Regular Monitoring
Frequent veterinary check-ups and blood tests are crucial for monitoring your dog’s blood sugar levels and overall health. Early detection of any imbalances allows for prompt adjustments to their treatment plan.
Understanding the link between canine cancer and blood sugar levels offers a new perspective on managing your dog’s health. By maintaining balanced blood sugar levels through proper diet, exercise, and veterinary care, you can create a healthier environment that may help prevent or slow the progression of cancer. Stay proactive and informed to ensure your furry friend enjoys a long, healthy life.

by TCMVET | Jul 3, 2024 | Dog Cancer & Tumors
In the realm of alternative treatments for canine cancer, magnet therapy has emerged as a promising option for pet owners seeking holistic approaches to enhance their dog’s health and well-being. This article delves into the potential benefits of magnet therapy for dogs with cancer, how it works, and what you should consider before integrating it into your pet’s treatment plan.
What is Magnet Therapy?
Magnet therapy, also known as magnetic field therapy, involves the use of static magnetic fields to improve health. In humans, it has been used to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and enhance overall well-being. For dogs, the concept is similar: applying magnets to specific areas of the body may help manage symptoms and support the healing process.
How Magnet Therapy Works for Dogs
Magnet therapy is believed to work by stimulating blood flow and enhancing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to tissues. This increased circulation can help reduce inflammation and pain, which are common issues in dogs with cancer. Additionally, magnets are thought to influence cellular function, potentially promoting the body’s natural healing processes.
Benefits of Magnet Therapy for Dogs with Cancer
1. Pain Relief
Cancer often causes significant discomfort in dogs. Magnet therapy can help alleviate pain by increasing blood flow to affected areas, reducing muscle tension, and promoting the release of endorphins—natural painkillers produced by the body.
2. Reduced Inflammation
Inflammation is a major concern in canine cancer, contributing to pain and the progression of the disease. Magnet therapy’s ability to enhance circulation may help reduce inflammation, leading to improved comfort and mobility for your pet.
3. Enhanced Healing
By promoting better blood flow and oxygenation, magnet therapy can support the healing of tissues damaged by cancer or its treatments, such as surgery or radiation. This can aid in faster recovery times and improved overall health.
4. Non-Invasive and Drug-Free
One of the significant advantages of magnet therapy is that it is non-invasive and does not involve pharmaceuticals, making it a suitable option for dogs that may not tolerate traditional medications well.
Considerations and Precautions
Before starting magnet therapy for your dog, it is crucial to consult with a veterinarian, preferably one experienced in holistic and alternative treatments. Here are some considerations:
1. Professional Guidance
A veterinarian can provide guidance on the appropriate type and strength of magnets to use, as well as the correct placement and duration of treatment to ensure safety and efficacy.
2. Individual Response
Not all dogs may respond to magnet therapy in the same way. Monitoring your dog’s response and adjusting the treatment as needed is essential for optimal results.
3. Complementary Treatment
Magnet therapy should be viewed as a complementary treatment rather than a standalone solution. It can be integrated with conventional cancer treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery to enhance overall outcomes.
How to Get Started
If you’re interested in exploring magnet therapy for your dog, start by discussing it with your veterinarian. They can recommend reputable products and provide instructions tailored to your dog’s specific condition and needs.
Magnet therapy offers a unique and innovative approach to managing canine cancer, providing benefits such as pain relief, reduced inflammation, and enhanced healing. As with any treatment, professional guidance and careful monitoring are essential to ensure the best outcomes for your beloved pet. By considering magnet therapy as part of a comprehensive cancer care plan, you can help improve your dog’s quality of life and support their journey to better health.

by TCMVET | Jul 3, 2024 | Dog Cancer & Tumors
When it comes to canine health, cancer is a formidable adversary that can wreak havoc on multiple systems within the body. One often overlooked aspect of this disease is its profound impact on the cardiovascular system. Understanding how cancer can affect your dog’s heart and blood vessels is crucial for early detection, effective treatment, and overall well-being.
How Cancer Affects the Cardiovascular System
1. Direct Invasion of Cardiac Tissues
Certain cancers, such as hemangiosarcoma, originate in the blood vessels and can directly invade the heart. Hemangiosarcoma commonly affects the spleen, liver, and heart, particularly the right atrium. This aggressive cancer can lead to significant cardiovascular complications, including pericardial effusion, where fluid accumulates around the heart, impeding its normal function.
2. Metastasis to the Heart and Blood Vessels
Cancer cells from primary tumors in other parts of the body can metastasize to the heart and blood vessels. This spread can cause blockages, disrupt blood flow, and lead to secondary tumors within the cardiovascular system. The resulting strain on the heart can compromise its ability to pump blood efficiently.
3. Paraneoplastic Syndromes
Paraneoplastic syndromes are indirect effects of cancer that can significantly impact the cardiovascular system. These syndromes occur when tumors produce substances that interfere with normal bodily functions. For instance, some tumors can cause hypercoagulability, leading to an increased risk of blood clots. These clots can travel to the heart or lungs, causing life-threatening conditions such as pulmonary embolism.
Symptoms to Watch For
Detecting cardiovascular issues related to cancer in dogs requires vigilance. Symptoms to watch for include:
- Persistent Coughing: This can indicate fluid buildup in the lungs due to heart failure.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing can be signs of cardiovascular compromise.
- Lethargy and Weakness: A decline in energy levels may suggest poor blood circulation.
- Fainting or Collapsing: These severe symptoms require immediate veterinary attention.
- Swelling: Look for swelling in the abdomen or limbs, which could indicate fluid retention.
Diagnostic Approaches
Early diagnosis is key to managing cardiovascular complications in dogs with cancer. Diagnostic methods include:
- Echocardiography: This ultrasound-based technique allows veterinarians to visualize the heart’s structure and function, identifying tumors or fluid accumulation.
- Electrocardiography (ECG): An ECG can detect irregular heart rhythms caused by cancerous growths or paraneoplastic syndromes.
- Blood Tests: Comprehensive blood panels can reveal markers of heart stress or hypercoagulability.
- Imaging: X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs can provide detailed images of the heart and surrounding tissues, highlighting abnormalities.
Treatment Options
Treatment for cancer-related cardiovascular issues in dogs depends on the type and stage of cancer, as well as the severity of the cardiovascular involvement. Options include:
- Surgery: Removing tumors that directly invade the heart or blood vessels can relieve symptoms and improve heart function.
- Chemotherapy: This systemic treatment can shrink tumors and slow their spread, alleviating cardiovascular strain.
- Radiation Therapy: Targeted radiation can reduce tumor size and mitigate its impact on the heart.
- Medications: Drugs that manage heart failure, control arrhythmias, or prevent blood clots are essential in supportive care.
Understanding the complex relationship between canine cancer and the cardiovascular system is vital for pet owners and veterinarians alike. By recognizing the symptoms, utilizing advanced diagnostic tools, and pursuing appropriate treatments, we can improve the quality of life for dogs battling this dual health challenge. Stay vigilant and proactive in your dog’s healthcare to ensure they receive the best possible care.
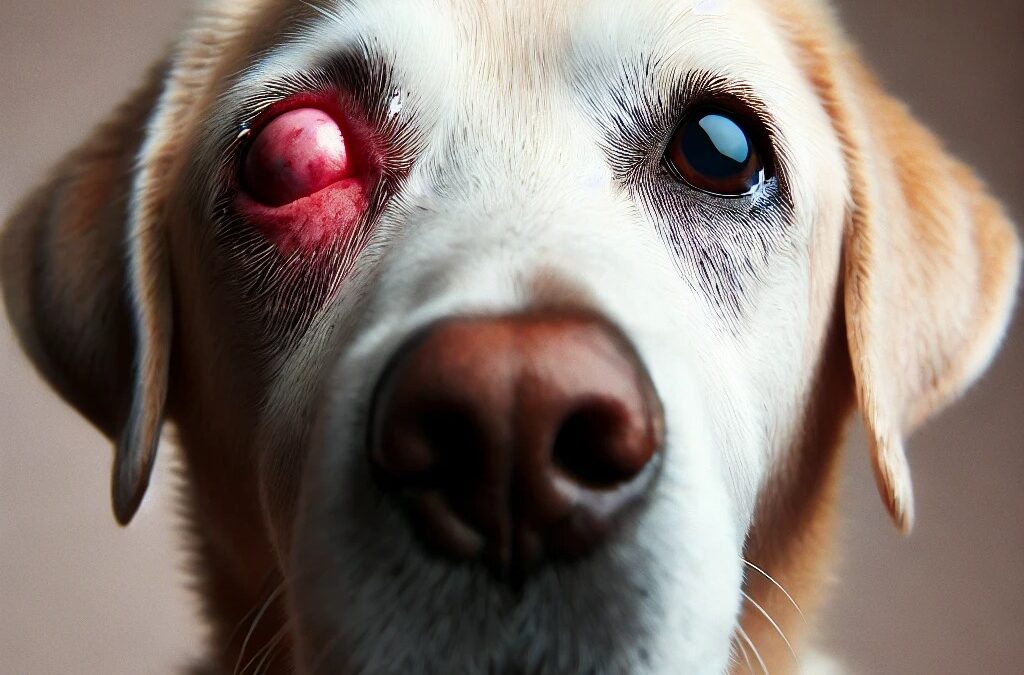
by TCMVET | Jul 3, 2024 | Dog Cancer & Tumors
Cancer in dogs can lead to a variety of health complications, including blindness. This article explores how different types of cancer can affect a dog’s vision, the symptoms to watch for, and the importance of early detection and treatment.
How Cancer Can Cause Blindness in Dogs
- Ocular Tumors: Tumors can develop directly within the eye, affecting structures such as the retina, optic nerve, or other critical components responsible for vision. Common ocular cancers include melanoma, lymphoma, and adenocarcinoma. These tumors can cause significant damage to the eye, leading to partial or complete blindness. Symptoms may include visible masses on the eye, redness, swelling, or changes in eye color.
- Brain Tumors: Tumors located in the brain, particularly in areas affecting the optic nerves or visual cortex, can disrupt a dog’s ability to see. The optic nerves transmit visual information from the eyes to the brain, and any pressure or damage from a tumor can impair this process. Symptoms might include sudden vision loss, changes in behavior, seizures, or head tilting.
- Metastatic Cancer: Cancer that originates in other parts of the body can spread (metastasize) to the eyes or brain, leading to similar issues as primary tumors in these locations. Metastatic cancer often progresses rapidly, making early detection and intervention crucial.
- Paraneoplastic Syndromes: These are indirect effects of cancer that can impact various parts of the body, including the eyes. Certain cancers can cause immune system reactions that damage ocular tissues, resulting in vision loss.
Symptoms to Watch For
If your dog has cancer, it’s important to monitor for signs of vision problems. Symptoms indicating potential blindness include:
- Squinting or closing one eye
- Excessive tearing or discharge
- Redness or swelling around the eyes
- Cloudiness or visible masses on the eye
- Behavioral changes such as bumping into objects or hesitancy to move in dim light
- Sudden or gradual loss of vision
Diagnosis and Treatment
Early detection and intervention are key to managing cancer-related blindness in dogs. Diagnostic methods include:
- Physical Examination: A thorough eye exam by a veterinarian to check for abnormalities.
- Imaging: Techniques such as MRI, CT scans, or ultrasound to detect tumors in the eyes or brain.
- Biopsy: Taking a sample of the tumor to determine its type and guide treatment.
Treatment options vary depending on the type and location of the cancer. They may include:
- Surgery: Removal of the tumor to prevent further damage and potentially restore vision.
- Radiation Therapy: Targeting the tumor with radiation to shrink it and reduce its impact on vision.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to treat cancer and slow its progression.
- Palliative Care: For advanced cases, focusing on maintaining comfort and quality of life.
Cancer can significantly impact a dog’s vision, leading to partial or complete blindness. Understanding the connection between cancer and blindness, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking prompt veterinary care are crucial steps in managing this condition. By staying informed and proactive, you can help ensure your dog receives the best possible care.







