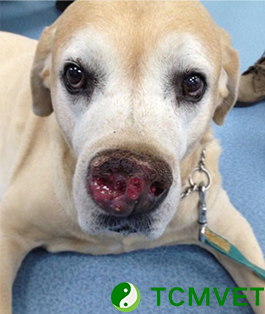
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC) is a prevalent form of cancer in small animals, especially in cats and dogs. This malignancy, arising from the squamous cells lining the skin or various internal organs, poses significant health challenges. However, recent advancements in veterinary oncology and related research are bringing new hope to pet owners and veterinarians. This article explores the latest developments in SCC research and how they are reshaping the treatment and management of this condition in small animals.
1. Targeted Therapies and Precision Medicine:
Advancements in understanding the molecular basis of SCC have paved the way for targeted therapies. Precision medicine, which involves tailoring treatment based on the individual pet’s genetic makeup, is gaining traction. Researchers are identifying specific genetic mutations and pathways involved in SCC, which could lead to more effective, customized treatment plans with potentially fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
2. Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy, a treatment that harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer, is a significant breakthrough in human oncology and is now being explored in veterinary medicine. This approach includes the development of cancer vaccines and immune checkpoint inhibitors that can help the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells more effectively.
3. Advanced Imaging Techniques:
The use of advanced imaging techniques such as PET scans and high-resolution MRI is improving the ability to diagnose and stage SCC in small animals. These technologies offer more detailed and accurate insights into the tumor’s size, spread, and response to treatment, allowing for more precise surgical planning and treatment monitoring.
4. Nanotechnology:
Nanotechnology in cancer treatment is an emerging field that holds promise for treating SCC in pets. Nanoparticles can be designed to target cancer cells specifically, delivering drugs directly to the tumor and reducing the impact on healthy tissues. This approach could lead to more effective treatments with fewer side effects.
5. Enhanced Surgical Techniques:
Surgical intervention remains a cornerstone in treating SCC, and advancements in surgical techniques are improving outcomes. Minimally invasive surgeries, guided by advanced imaging, allow for more precise tumor removal with quicker recovery times. Laser surgery is another area of advancement, offering a less invasive option with less bleeding and reduced pain.
6. Better Understanding of Environmental Factors:
Research into the environmental and lifestyle factors contributing to SCC, such as sun exposure and chemical exposure, is helping in the development of better preventive strategies. This includes public awareness campaigns on the importance of protecting pets from excessive sun exposure and avoiding harmful chemicals.
7. Holistic and Supportive Care:
There is an increasing focus on holistic approaches and supportive care in managing SCC. This includes nutritional support, pain management, and alternative therapies like acupuncture and herbal medicine, which can complement traditional treatments and improve the quality of life for pets with cancer.
The landscape of SCC treatment in small animals is evolving rapidly, thanks to ongoing research and technological advancements. These developments not only promise more effective and targeted treatments but also emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach that includes prevention and supportive care. For pet owners and veterinarians, staying informed about these advancements is key to providing the best possible care for pets with SCC.